Figure 1.
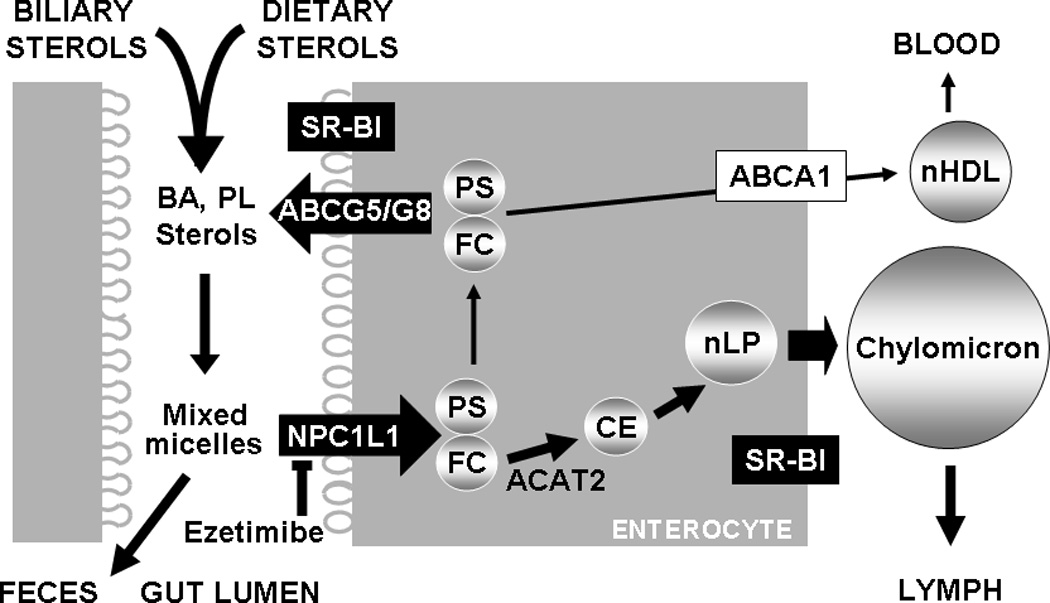
Intestinal sterol absorption and secretion. Sterols including free cholesterol (FC) and free plant sterols (PS) from diet and bile are mixed with phospholipids (PL) and bile acids (BA) to form micelles. FC and PS solubilized in mixed micelles are transported into absorptive enterocytes via an NPC1L1-dependent and ezetimibe-inhibitable mechanism. FC is delivered to the ER for esterification by acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase-2 (ACAT2) to form cholesterol esters (CE) that is then packaged into nascent lipoprotein particles (nLP) and secreted as a constituent of chylomicron. PS and FC that escapes ACAT2 esterification may be directly transported to nascent HDL (nHDL) through basolateral ABCA1, or back to the gut lumen via ABCG5/G8.
