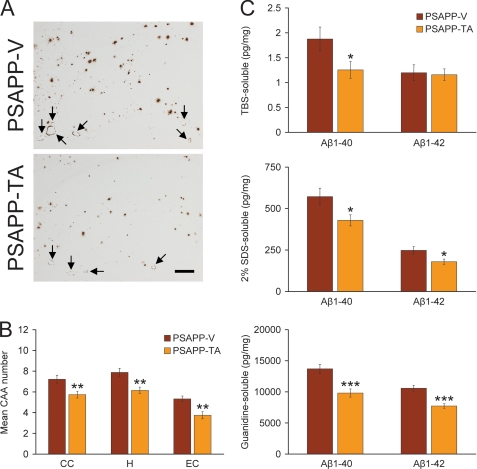
FIGURE 4.
Cerebral vascular β-amyloid deposits and brain Aβ levels are reduced in PSAPP mice given oral tannic acid treatment. A, representative photomicrographs of 4G8 immunohistochemistry were taken from PSAPP-V and PSAPP-TA mouse hippocampi at 12 months of age, and cerebral vascular β-amyloid deposits are indicated (arrows). Scale bar denotes 200 μm. B, severity of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (mean CAA deposit number per mouse) is shown on the y axis with the brain region indicated on the x axis (CC, H, and EC). C, TBS-soluble, 2% SDS-soluble, and TBS-insoluble (but 5 m guanidine HCl-extractable) fractions from three-step extracted brain homogenates were examined by sandwich ELISA for human Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 levels. Data were obtained from PSAPP mice treated with vehicle (PSAPP-V, n = 16) or with TA (PSAPP-TA, n = 16) for 6 months commencing at 6 months of age. All statistical comparisons are within the brain region and/or between PSAPP-V and PSAPP-TA mice.