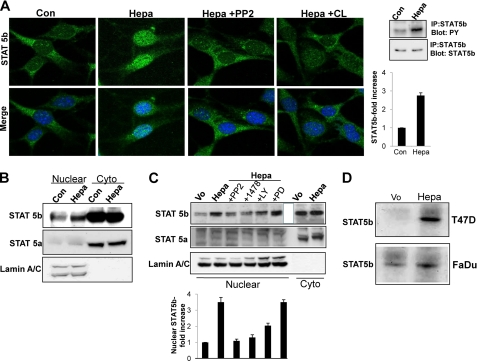
FIGURE 2.
STAT5b phosphorylation and nuclear translocation by heparanase is mediated by SRC and EGFR. A, inhibition study. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts were left untreated (Con) or were incubated with heparanase without (Hepa) or after the cells were preincubated with PP2 (5 μm) or CL-387785 (CL; 0.1 μm) for 30 min. Following a 1-h incubation with heparanase, cells were fixed and stained with anti-STAT5b antibody (upper panels). Merge images with DAPI counter staining (blue) are shown in the lower panels. Original magnification, ×63. Corresponding control (Vo) and heparanase-transfected cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-STAT5b antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-phosphotyrosine (PY) or anti STAT5b antibodies (rightmost panels). Densitometry analysis of pSTAT5b is shown in the right lower panel. B, control (Con) and heparanase-treated (Hepa) cells from corresponding cultures were fractionated into nuclear and cytoplasmic (Cyto) fractions and subjected to immunoblotting applying antibodies directed against STAT5b (upper panel), STAT5a (middle panel), and lamin A/C to validate fraction purity and protein loading (lower panel). C, heparanase-transfected FaDu cells were left untreated (Hepa) or incubated (4 h) with SRC (PP2, 5 μm), EGFR (1478, 5 μm), PI3K (LY, 15 μm), or MEK (PD, 10 μm) inhibitors. Nuclear fractions were then prepared and subjected to immunoblotting applying anti-STAT5b (upper panel), anti-STAT5a (second panel) and anti-lamin A/C (third panel) antibodies. Nuclear fraction of control (Vo) cells and cytoplasmic fractions (Cyto) of control (Vo) and heparanase-transfected (Hepa) cells were included as control. Densitometry analysis of nuclear STAT5b levels is shown in the lower panel. D, DNA binding. Nuclear extracts of control (Vo) and heparanase-transfected (Hepa) T47D (upper panel) and FaDu (second panel) cells were incubated (20 h, 4 °C) with biotinylated oligonucleotides containing the STAT5 binding site of the bovine β-casein promoter. Strepavidin-agarose beads were then added for 60 min, and, after washing, agarose-bound material was subjected to immunoblotting with anti-STAT5b antibody. Note the increased STAT5b association with the casein gene promoter following heparanase overexpression.