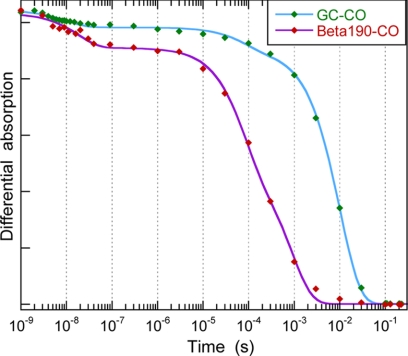
FIGURE 5.
Bimolecular rebinding of CO to full-length sGC and to β1(190) after CO photo-dissociation. The differential absorption kinetics were probed at 450 nm and are normalized. The fast minor decay at ∼10–20 ns is due to CO geminate rebinding, including the picosecond phase. The slower phase, with much larger amplitude, is the bimolecular rebinding of CO. The data were fitted to a sum of three exponentials, and the fitted time constants are listed in Table 2. The maximum of the signal corresponds to the temporal coincidence of the photo-dissociating and probing pulses. The pressure of pure CO in the gaseous phase above the sample is 1.3 bar, yielding a concentration of 1.33 mm in the aqueous phase at 20 °C.