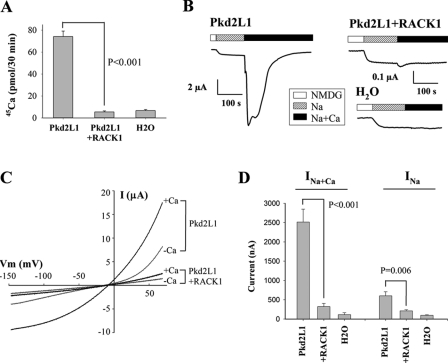
FIGURE 4.
Functional modulation of Pkd2L1 channel by RACK1. A, radiolabeled 45Ca uptake in oocytes expressing Pkd2L1 + RACK1 or Pkd2L1 alone and H2O-injected control oocytes. Radiolabeled 45Ca uptake was performed using uptake solution 3 days following RNA injection. Data were averaged from three experiments. The effect of RACK1 was analyzed by unpaired t test. B, representative whole-cell current tracings under voltage clamp (Vm = −50 mV) using the two-microelectrode voltage clamp technique. Different scales of current were used as indicated. Currents were measured using solution “Na” (the standard Na+-containing solution (100 mm NaCl, 2 mm KCl, 1 mm MgCl2, 10 mm Hepes, pH 7.5) or “Na+Ca” (standard Na+-containing solution + 5 mm CaCl2) by the two-microelectrode voltage-clamp technique with a voltage ramp protocol. C, representative current-voltage curves in an oocyte expressing Pkd2L1 alone or Pkd2L1 + RACK1 in the presence of the standard Na+-containing solution with (+Ca) or without (−Ca) 5 mm CaCl2 as indicated. D, averaged currents obtained in oocytes expressing Pkd2L1 + RACK1 (n = 17) or Pkd2L1 alone (n = 17) and H2O-injected control oocytes (n = 6) in the presence of Na+-containing solution with (Na+Ca) or without (Na) addition of 5 mm CaCl2. Inhibition of currents by RACK1 was very significant both with and without Ca2+ with p < 0.001 and p = 0.006 (unpaired t test), respectively. Two-way analysis of variance found that the inhibitory effect of RACK1 is very significant (p < 0.001), that the stimulatory effect of Ca2+ is very significant (p < 0.001), and that the effect of RACK1 is significantly different (p < 0.001) whether Ca2+ is present or not in the solution, consistent with t test analysis. Error bars indicate S.E.