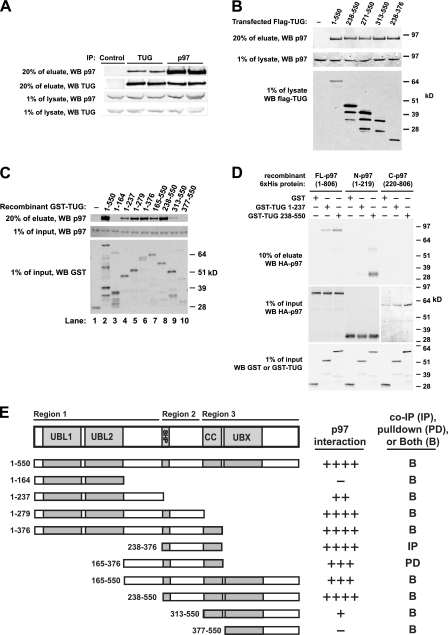
FIGURE 1.
Interaction of TUG and p97. A, anti-TUG or anti-p97 antibodies were used to immunoprecipitate (IP) endogenous TUG and p97 from HEK293 cells lysed using 0.5% Nonidet P-40. Control IgG was used in lane 1, and duplicates of TUG (lanes 2 and 3) and p97 (lanes 4 and 5) immunoprecipitates are shown. Eluates and preimmunoprecipitation lysates were immunoblotted to detect TUG and p97, as indicated. B, HEK293 cells were transfected to express FLAG-tagged TUG proteins containing the indicated residues and lysed using 0.5% Nonidet P-40, and immunoprecipitations were performed using an anti-FLAG affinity matrix. Endogenous p97 was immunoblotted in eluates and pre-immunoprecipitation lysates, as indicated. C, recombinant GST or GST-TUG proteins containing the indicated TUG residues were used to pull down recombinant His6-p97 in 0.5% Nonidet P-40 buffer. Eluates and input proteins were immunoblotted using anti-p97 and anti-GST antibodies as indicated. D, GST or GST-TUG proteins were used to pull down His6-HA-tagged full-length, N-terminal, or C-terminal p97 proteins in 0.5% Nonidet P-40 buffer. Eluates and inputs were immunoblotted using anti-GST and anti-HA antibodies as indicated. Residues present in each p97 and TUG protein are indicated. E, diagram summarizes binding of p97 to TUG proteins containing the indicated residues. For reference, the overall TUG domain structure is shown at top. The relative amount of p97 that associated with each TUG protein is indicated at the right. Binding was tested using both GST pull-downs (PD; as in C and D) and by immunoprecipitation (IP; as in B). Most interactions were tested both ways, as indicated (B), and similar results were obtained using both methods. Each construct was tested at least twice, with most tested three times. WB, Western blot.