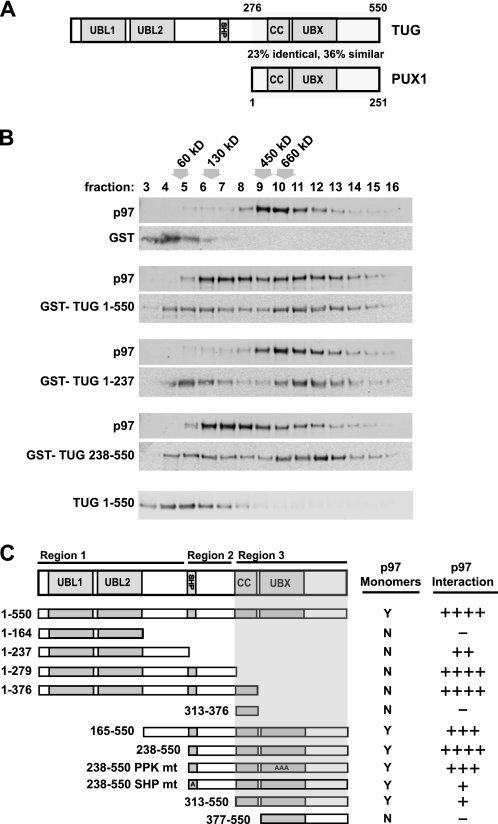
FIGURE 2.
TUG generates p97 monomers. A, diagrams of the domain structures of TUG and PUX1; a region of similarity is indicated. The full alignment is shown in supplemental Fig. 1. B, recombinant His6-p97 proteins were incubated with GST alone or with the indicated GST-TUG proteins in equimolar amounts. After 30 min at 4 °C, p97 complexes were separated by sedimentation on sucrose gradients and analyzed by immunoblotting for p97 and TUG, as indicated. Fractions are numbered from the top of the gradient, and the positions of molecular weight standards are indicated above the fraction numbers. The position on the gradient of TUG alone is shown at the bottom. C, the diagrammed TUG proteins were expressed as recombinant GST fusions and were tested for their ability to generate p97 monomers using sedimentation. A 3:1 molar ratio of TUG/p97 proteins was used. All constructs were tested at least twice. The shaded area corresponds to the region of TUG that was necessary for generation of p97 monomers. For reference, the relative ability of each TUG construct to copurify p97 in pull-down and/or coimmunoprecipitation experiments is shown at the right.