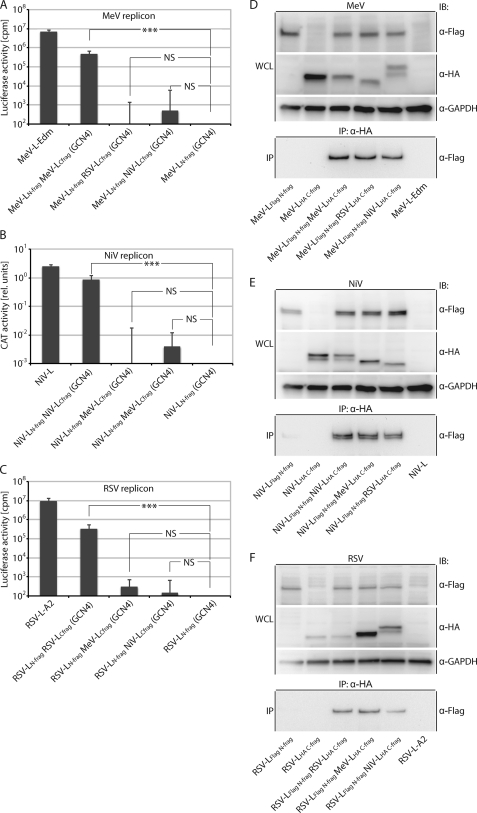
FIGURE 5.
Functional trans-complementation mandates homotypic L fragment combinations. A–C, shown are homo- and hetero-complementation assays after co-transfection of plasmids encoding GCN4 domain-tagged MeV, NiV, or RSV L N- and C-terminal fragments in all combinations in the context of the MeV (A), NiV (B), or RSV (C) replicon reporter systems. Values show relative luciferase or CAT activities and represent the averages of at least three independent experiments ± S.D. Control cells received the respective LN-frag expression plasmid-only instead of the homotypic standard L or co-transfection of LN-frag and LC-frag encoding plasmids. Statistical analysis assesses the significance of deviation of the different L fragment combinations from the controls (***, p < 0.001; NS, not significant). D–F, all homo- and heterotypic L N- and C-fragment combinations analyzed in A–C efficiently co-immunoprecipitate. Whole cell lysates (WCL) of BSR-T7/5 cells expressing the GCN4-tagged homo- and heterotypic L fragment pairs as specified were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-HA antibodies followed by gel fractionation and immunoblotting (IB) using anti-FLAG antibodies. In parallel, lysates were directly analyzed using HA-, FLAG-, or cellular GAPDH-specific antibodies. Controls received expression plasmids encoding standard, untagged L in place of the epitope-tagged L variants.