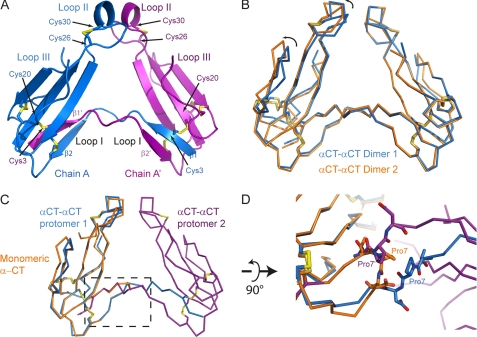
FIGURE 1.
X-ray structure of dimeric αCT. A, αCT-αCT dimer is composed of two protomers represented in blue and purple, respectively. The β1 strand from the first protomer is extended away from the toxin core and swapped with the β1 strand from the second protomer. Disulfide bridges between Cys3 from one protomer and Cys20 from the second protomer stabilize the dimeric toxin. B, ribbon representation of two αCT-αCT dimers, reconstituted from our structural data, superposed with respect to one of the protomers. The variability between the two dimers likely reflects the flexibility between the two toxin cores. C, ribbon representation of the superposition of monomeric αCT in orange on a protomer of the dimeric αCT (blue and purple). The boxed region is a zoomed in view rotated 90° around a horizontal axis in D. Pro7 from monomeric αCT (in orange) or from either protomer of the αCT-αCT dimer (blue and purple) is depicted as sticks. In the dimeric form, the Pro7 is extended away from the toxin core whereas in the monomeric αCT, Pro7 makes a turn.