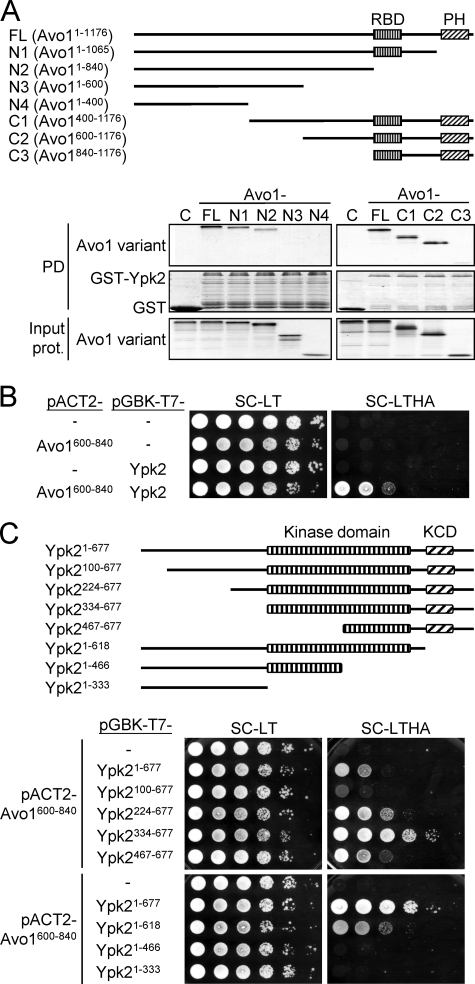
FIGURE 6.
Mapping of the Avo1-Ypk2 interaction regions. A, GST pulldown assay for the Avo1-Ypk2 interaction. A schematic representation of the tested Avo1 deletion mutants is shown. RBD, Raf-like Ras-binding domain; PH, pleckstrin homology domain. 35S-Labeled Avo1 variants were prepared using an in vitro transcription/translation kit. Equal amounts of each 35S-labeled Avo1 fragment were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose bead-bound GST or GST-Ypk2. Pulled down proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography; GST and GST-Ypk2 were visualized by Coomassie Blue staining. One-twentieth amount of the input 35S-labeled proteins used in the pulldown (PD) procedures were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography and shown in the bottom panels. B, yeast two-hybrid assay for the interaction between Avo1600–840 and Ypk2. 10-fold serial dilutions of yeast suspensions were spotted on plates and incubated at 27 °C until colonies formed. Yeast cells containing both pACT2- and pGBK-T7-derived plasmids can grow on the Leu- and Trp-dropout SC medium (SC-LT). Growth on a reporter medium lacking His and Ade (SC-LTHA) indicates interaction between the two test proteins. C, yeast two-hybrid assay for the interaction between Avo1600–840 and different regions of Ypk2. A schematic representation of the tested Ypk2 deletion mutants is shown. KCD, AGC-kinase C-terminal domain. The spot assay was performed as in B. The SC-LTHA reporter plate at the bottom was incubated longer than the upper one to better demonstrate cell growth resulting from the interaction between Avo1600–840 and Ypk21–618.