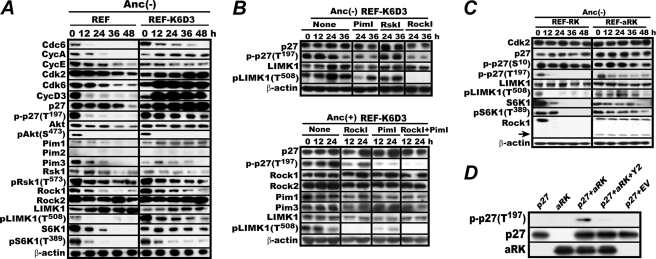
FIGURE 3.
ROCK1 phosphorylates C-terminal Thr197 of p27. A, ROCK is active in anchorage-deprived REF-K6D3. The same experiment as in Fig. 1 was carried out with immunoblot analysis of the indicated factors. B, treatment with Y29762, a specific ROCK inhibitor, diminishes p27 Thr197 phosphorylation. REF-K6D3 was incubated in MC for 12 h and then with no inhibitor, 20 μm GW5074, 20 μm BI-D1870, or 30 μm Y27632 for an additional 36 h. The cells were lysed and analyzed for p27 Thr197 phosphorylation. C, in REF expressing an active ROCK1, Thr197 phosphorylation of p27 persists during anchorage deprivation. REF-RK and REF-aRK were cultured in MC and analyzed for the indicated factors as in Fig. 2A. The arrow indicates the constitutively active truncated ROCK1. D, E. coli-expressed active ROCK1 phosphorylates E. coli-expressed p27 Thr197 in vitro. N-terminal histidine oligomer-tagged, C-terminal-truncated aRK was incubated with similarly tagged p27 or its E. coli empty vector control lysate (EV) in the reaction mixture for 30 min with or without the addition of 50 μm Y29762 (Y2) as described (17) and analyzed for p27 Thr197 phosphorylation by immune-blotting.