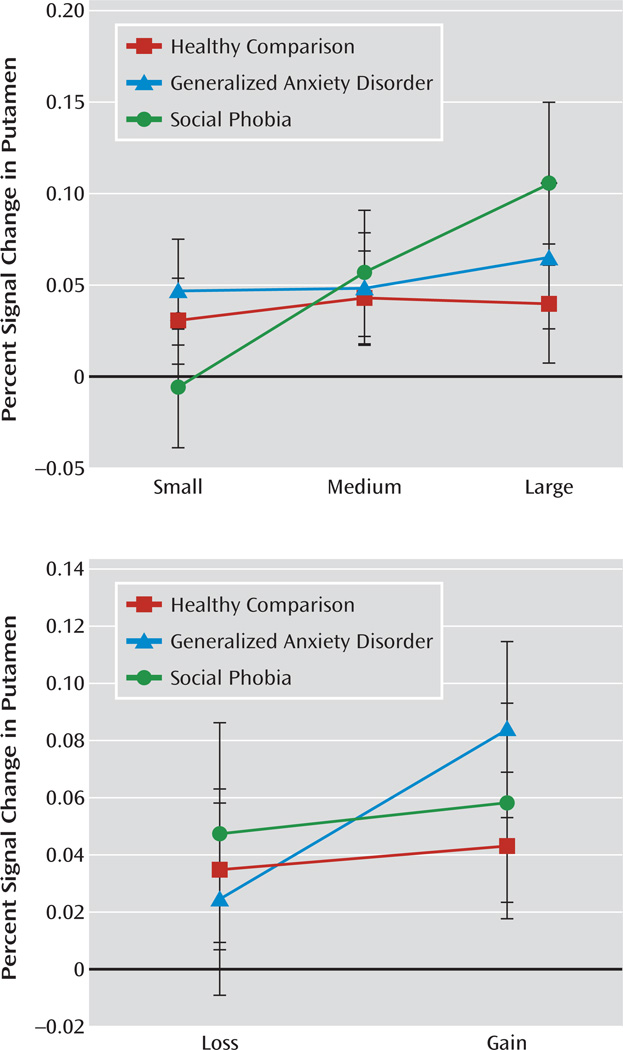
FIGURE 3.
Event-Related Percent BOLD Signal Chang e Extracted From the Putamen Region of Interest Among Adolescents With Social Phobia or Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Age-Matched Healthy Comparison Subjects a
a The top graph depicts a significant group-by-magnitude interaction effect (F=3.94, df=2, 55, p=0.03). Within the social phobia group, but not the generalized anxiety disorder or healthy comparison group, putamen activation increased as incentive magnitude increased from small to medium (p=0.02) and small to large (p=0.001). The bottom graph depicts a significant group-by-valence interaction effect (F=3.21, df=4, 55, p<0.05). Within the generalized anxiety disorder group, but not the social phobia or healthy comparison group, putamen activation was significantly greater on gain versus loss trials (p=0.001). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.