Fig. 1.
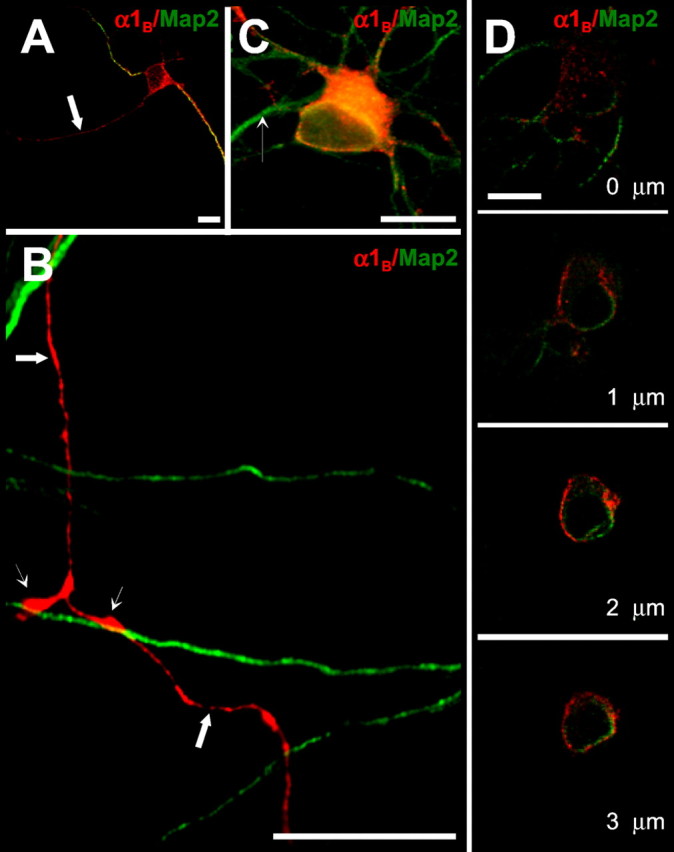
Distribution of recombinant N-type channels in immature hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal neurons cultured in high density were transfected with a mixture of HA-α1B/α2δ/β3 cDNAs 2 d after plating. At 4 d after transfection, the neurons were fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with monoclonal anti-HA (red) and polyclonal anti-MAP2 (green) antibodies for conventional (A–C) and confocal (D) imaging. Scale bars, 20 μm. A, Recombinant HA-α1B is targeted to both axons (arrow, MAP2-negative) and dendrites (MAP2-positive processes) of immature neurons. B, Recombinant HA-α1B is uniformly distributed in axons of transfected neurons (large arrows, MAP2-negative), with some degree of enrichment in zones of contacts between axons and dendrites of neighboring nontransfected cells (small arrows, MAP2-positive). C, Recombinant HA-α1B is present in cell bodies and dendrites of transfected neurons. The dendrite of a neighboring untransfected cell is indicated by a small arrow. Only weak HA immunoreactivity was typically observed in the proximal axonal segment. D, Confocal analysis of recombinant HA-α1B localization in the soma. Stacks of images were collected starting from the surface of the cell with 0.2 μm thickness. Every fifth image from the stack is shown.
