Figure 7.
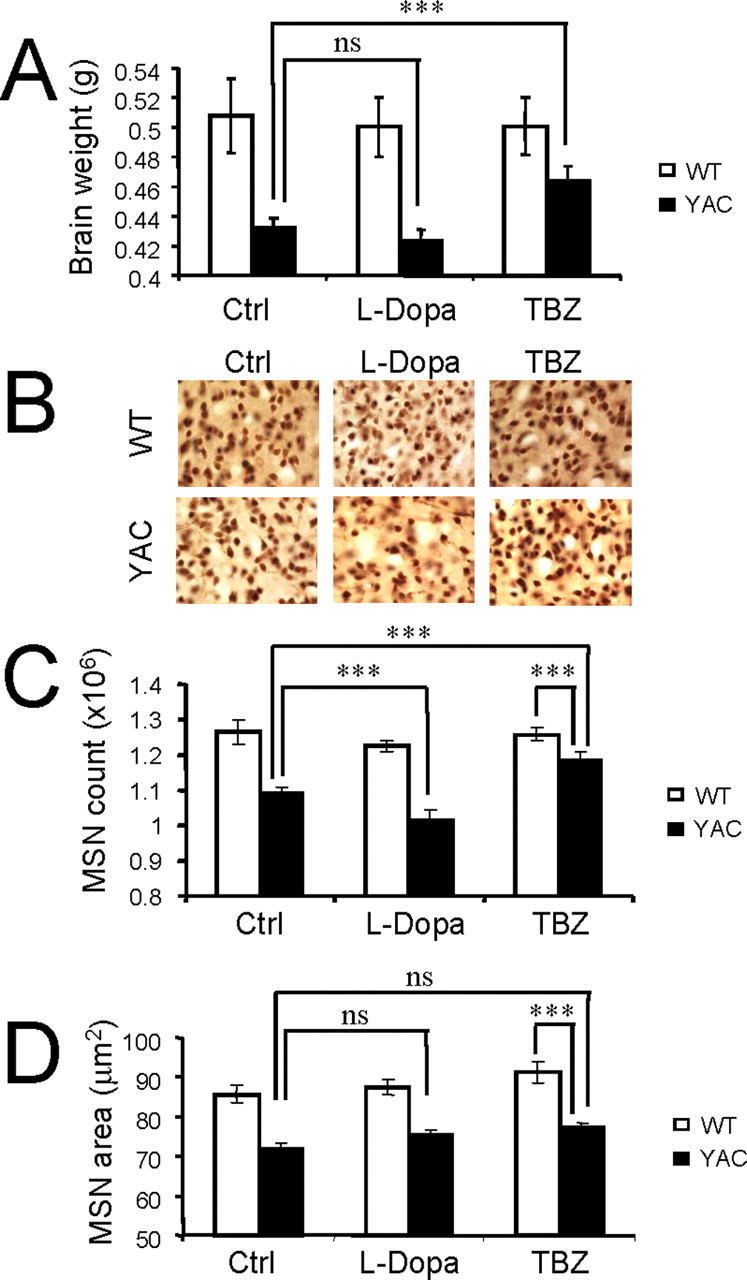
Effect of dopamine signaling on neuronal loss in YAC128 mice. A, Average brain weight of 11-month-old WT and YAC128 (4AC) mice. The brain weight of control YAC128 is significantly reduced compared with control WT group (p < 0.05). The brain weight of YAC128 mice fed with l-DOPA/TBZ is significantly increased compared with brain weight of control (Ctrl) YAC128 mice (***p < 0.05). B, Representative NeuN staining of striatal sections from 11-month-old WT and YAC128 mice. C, Average striatal neuronal counts of 11-month-old WT and YAC128 mice. Control YAC128 mice showed significant striatal neuronal loss (p < 0.05) compared with control WT mice. YAC128 mice fed with l-DOPA exhibited significant neuronal loss (***p < 0.05) compared with control YAC128 mice. YAC128 mice fed with l-DOPA/TBZ display significantly increased striatal neuronal counts compared with control YAC128 mice (***p < 0.05) but significantly reduced neuronal counts compared with WT mice (***p < 0.05). D, Average cross-sectional area of striatal neurons of 11-month-old WT and YAC128 mice. A, C, D, For each group of mice, the results are shown as mean ± SEM (for the number of mice in each group, see Table 3). Ctrl, Control; ns, not significant.
