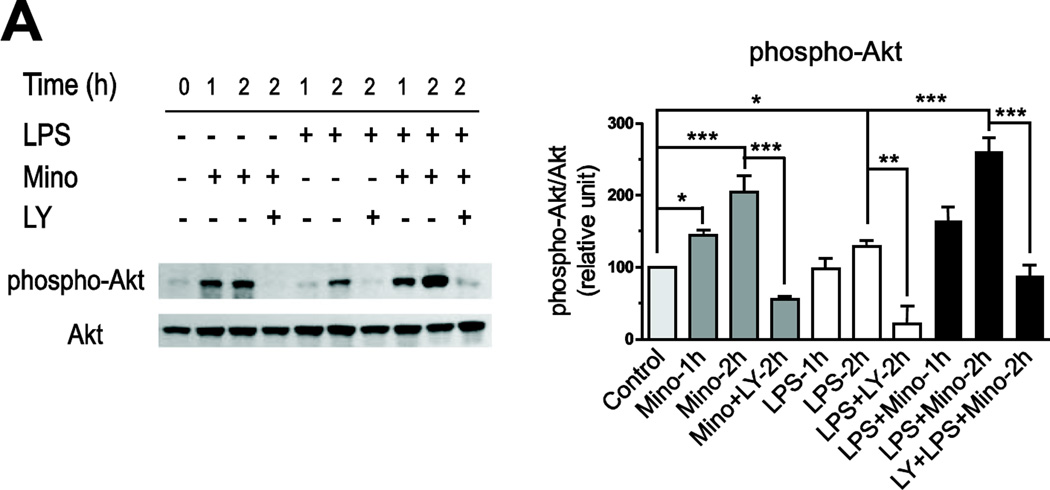
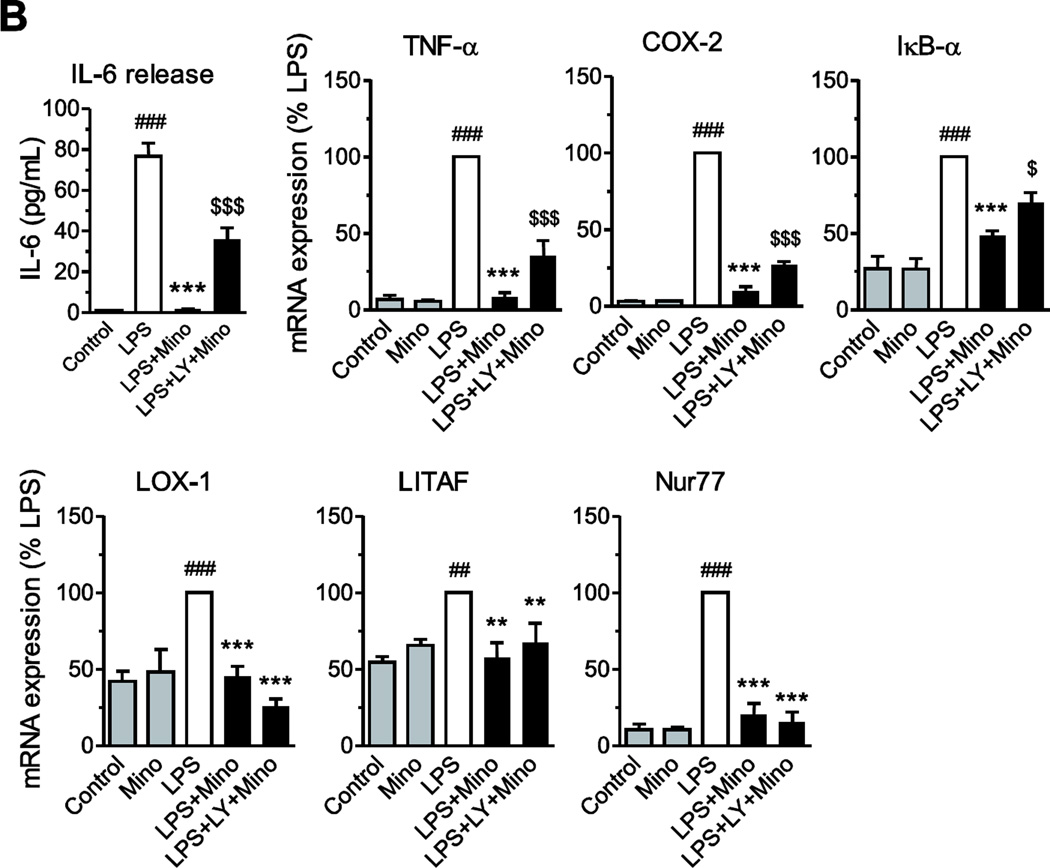
Fig. 8.
The anti-inflammatory effects of minocycline are partly mediated through Akt activation. (A) Minocycline (Mino) enhances Akt activity. Human monocytes were treated with minocycline (40 µM) alone, LPS (50 ng/ml) alone, or in combination (with minocycline being added 1 hr before LPS). The phosphorylation of Akt was determined at different time points as described in Materials and Methods. Minocycline alone or in combination with LPS increased phosphorylation of Akt in a time-dependent manner, and pretreatment with specific PI3K/Akt pathway inhibitor LY294002 (LY, 10 µM) prevented this effect. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (B) Monocytes were pretreated for 2 h with LY294002 (LY, 10 µM) before minocycline (40 µM) followed by LPS (50 ng/ml) incubation. After 4 h of LPS treatment, IL-6 release was quantified in culture medium by specific ELISA, and the mRNA expression of TNF-α, COX-2, IκB-α, LOX-1, LITAF and Nur77 (C) was quantified by RT-PCR as described in Material and Methods. Data are presented as means ± SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined with one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls posttest. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with LPS; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 compared with Control; $P<0.05, $$$P<0.001 compared with LPS+Mino.