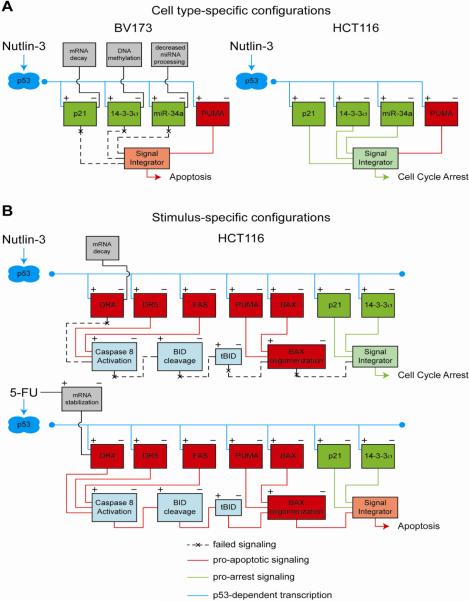
Figure 6. Context-dependent configurations of the p53 circuit board define the efficacy of p53 based therapies.
A. An example of cell type-specific p53 responses is provided by non-genotoxic p53 activation by Nutlin-3 across cancer cell lines. In BV173 cells (left), the cell cycle arrest integrated circuit is impaired by p21 mRNA decay, 14-3-3σ promoter methylation and impaired processing of miR-34a. In contrast, these three cell cycle arrest genes are effectively activated in HCT116 cells (right), where they function coordinately to establish a cell cycle arrest response, even though potent apoptotic genes such as PUMA have also been induced. B. Stimulus-specific assembly of the p53 circuit in response to p53 activation by Nutlin-3 versus 5-FU in HCT116 cells. Both Nutlin-3 and 5-FU strongly activate genes involved in both cell cycle arrest and apoptosis; however, only 5-FU treatment results in p53-independent stabilization of DR4 mRNA and concomitant upregulation of DR4 protein levels, which is required for caspase 8 activation and proteolytic activation of BID into tBID. Activation of the DR4:tBID axis by 5-FU drives the apoptotic response by promoting oligomerization of poised BAX at the mitochondria.