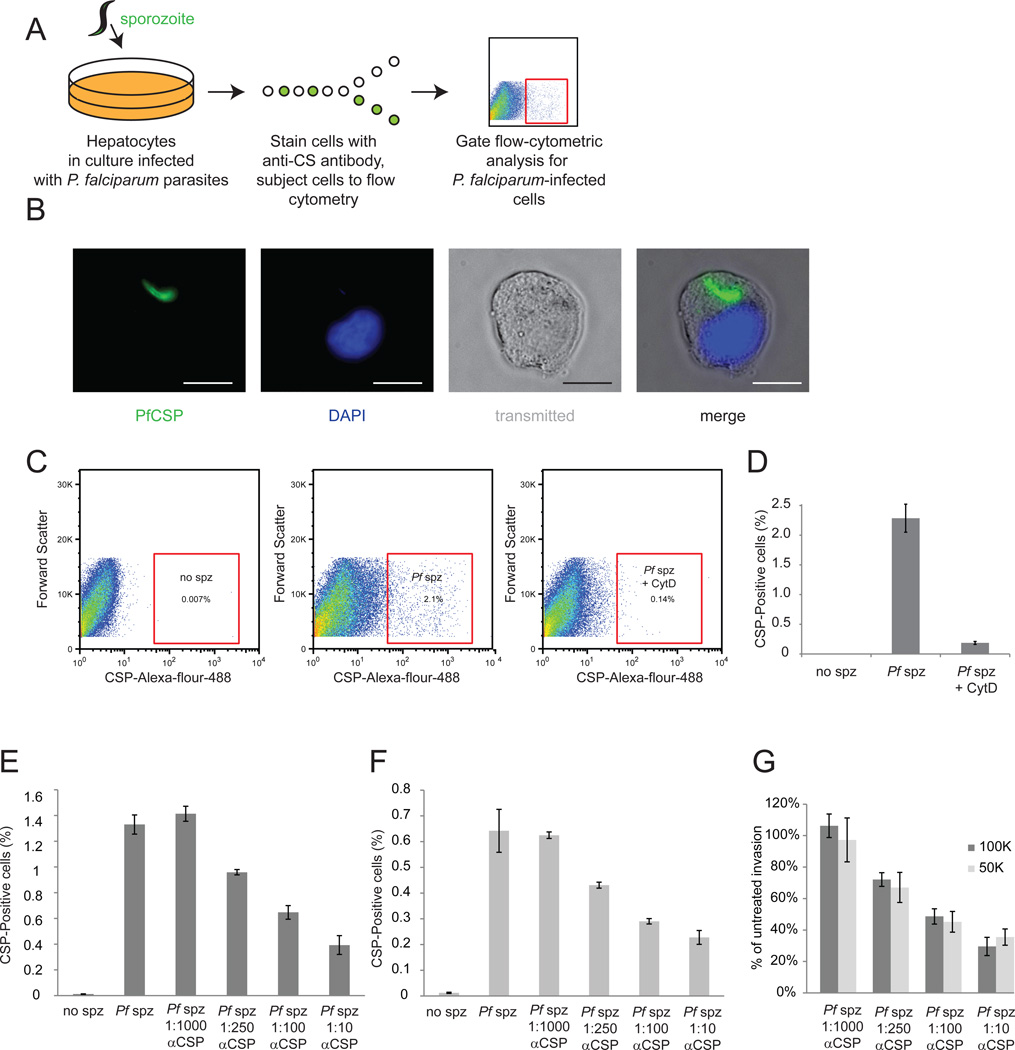
Figure 1. Flow-cytrometric analysis is efficient at monitoring P. falciparum liver-stage infection.
(A) Schematic describing methodology used. HC04 hepatocytes are grown in culture then infected with P. falciparum sporozoites. Cells are detached, fixed, permeablized and stained with a monoclonal antibody against circumsporozoite protein (CSP). Infected cells are identified by flow cytometric analysis. (B) Image of an infected cell isolated by FACS. Parasite CSP is stained green, and the host cell nucleus is visualized by DAPI in blue. Scale bar is 10 µm. (C) Scatter plots representing gating strategy for identifying infected cells. Live hepatocytes are first selected by forward and side scatter (not shown) and then hepatocytes with high levels of CSP selected. (D) P. falciparum sporozoites were incubated for 30 minutes with or without Cytochalasin D, and then used to infect HC04 hepatocytes. Cytochalasin D significantly inhibits parasite invasion. 100K (E) or 50K (F) P. falciparum sporozoites were incubated for 30 min without or with various dilutions of 2A10 CSP antibody, and then used to infect HC04 hepatocytes. Antibody pre-incubation with sporozoites decreases invasion rates in a dose-dependent manner. (G) Inhibition rates do not vary depending on invasion rates. To determine invasion rates, antibody-blocked rate was divided by untreated P. falciparum invasion rate for both 100,000 sporozoites (dark grey bars) and 50,000 sporozoites (light grey bars)