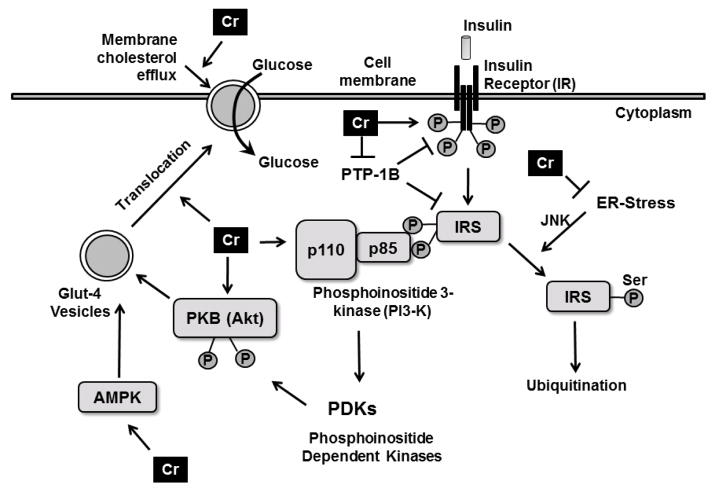
Figure 1.
Putative mechanisms by which chromium augments cellular glucose uptake. Chromium has been shown to enhance the kinase activity of insulin receptor β, to increase the activity of downstream effectors of insulin signaling pI3-kinase and Akt and to enhance Glut4 translocation to the cell surface. Chromium also down-regulates PTP-1B, the negative regulator of insulin signaling and alleviates ER-stress within the cells, rescuing IRS from JNK-mediated serine phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination. Transient upregulation of AMPK by chromium leads to increased glucose uptake. Chromium mediates cholesterol efflux from the membranes causing glut4 translocation and glucose uptake.