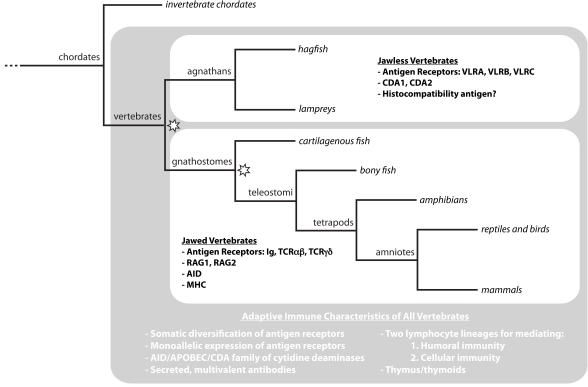
Fig. (1). Adaptive immunity throughout vertebrate phylogeny.
Vertebrates employ an adaptive strategy for immune defense that relies upon several universal characteristics. Jawless (agnathan) and jawed (gnathostome) vertebrate lineages differ, however, in several fundamental elements of adaptive immunity. Agnathans recognize antigens with VLRs constructed of LRR modules; CDA1 and CDA2 have been posited as critical mediators of VLR somatic diversification. Gnathostomes construct Ig and TCR antigen receptors from IgSF domains; in this lineage RAG1 and RAG2 are vital for gene assembly and AID for somatic hypermutation, class switching, and gene conversion. Two whole-genome duplications have been proposed during vertebrate evolution (indicated by stars).