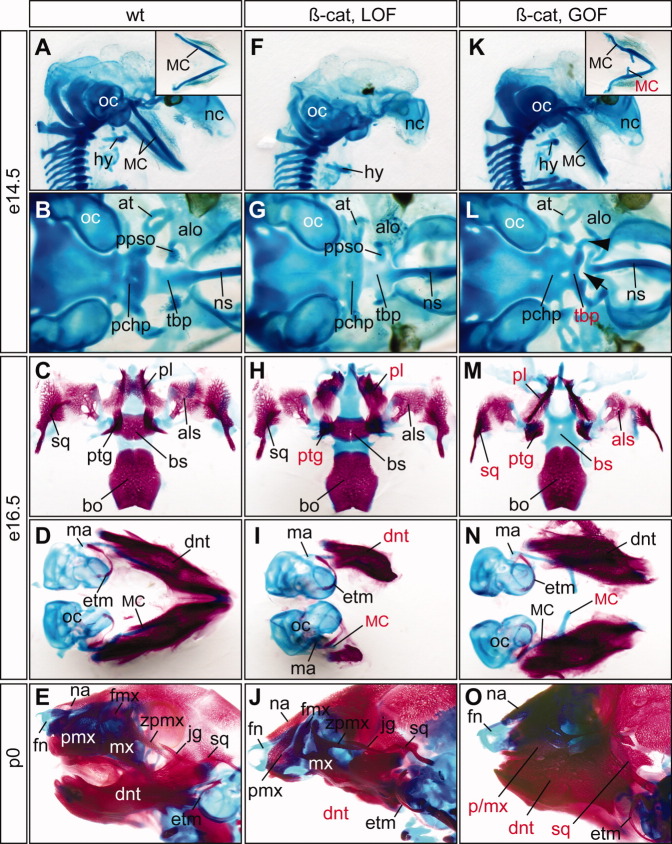
Fig. 4.
Cartilage and bone defects of epithelial-specific β-catenin mutants. A–O: Alcian blue cartilage staing of of embryonic day (E) 14.5 (A,B,F,G,K,L), E16.5 embryos (C,D,H,I,M,N), and newborn pups (E,J,O) and alizarin red bone staining of E16.5 embryos and newborn pups. A–E: Wild-type controls. F–J: β-cateLOF mutants display severe truncation of Meckel's cartilage (MC) and dentary bone, deformation of palatine (pl) and pterygoid (ptg). K–O: β-cateGOF mutants have ectopic MC and upper jaw defects. Red labels indicate defective structures. All pictures are ventral views except A, E, F, J, K and O, which are sagittal views. Inserts in A and K show ventral view of dissected MC. Note that the dentary bones of the β-cateGOF (N) are connected distally but dissociated during staining and dissection process. Arrow, gap; arrowhead, unidentified cartilage rod; at, ala temporalis; alo, ala orbitalis; als, alisphenoid; bo, basioccipital; bs, basisphenoid; dnt, dentary; etm, ectotympanic; fmx, frontal process of maxilla; fn, frontal nasal cartilage; hy, hyoid; jg, jugal; ma, malleus; mx, maxilla; mc, Meckel's cartilage; na, nasal bone; nc, nasal capsule; ns, nasal septum; oc, otic capsule; pchp, parachordal plate; pl, palatine; ppso, pila postoptica; ptg, pterygoid; sq, squamosal; tbp, trabecular basal plate; zpmx, zygomatic process of maxilla.