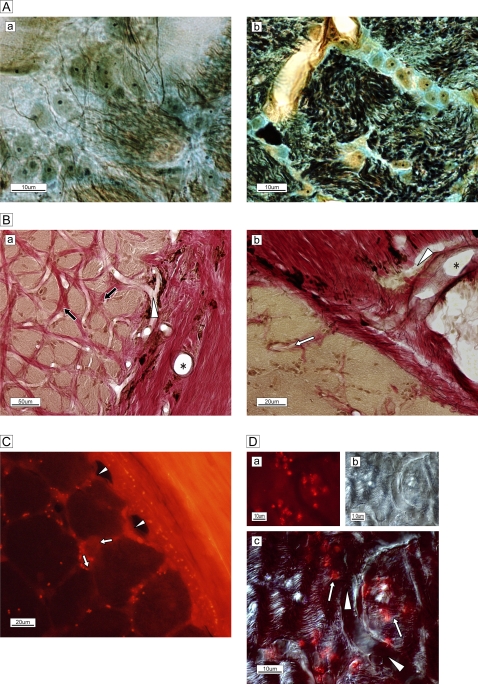
Figure 2.
(A) Silver–Luxol fast blue staining of the frontal section of the optic nerve in the lamina cribrosa. (a) Each bundle (brown) is surrounded by a column in the lamina cribrosa septa. (b) High-magnification view of the septa shows neurofilaments (black), numerous astrocytes with processes, oligodendrocytes (oval yellowish-brown cells with nuclei) and extracellular connective tissue (light blue) circumferentially enveloping the bundle (brown). (B) Elastica van Gieson staining of the extracellular matrix of the temporal border with the subarachnoid space of the optic nerve. (a) Arterioles are visible in the surrounding connective tissue (*). A capillary (white arrowhead) is visible and elastic (red) connective tissue (black arrows) is distributed in the column. (b) Magnified view of the site of penetration of an arteriole (*) and capillary (white arrowhead) into columnar spaces (white arrow). Bundles are stained brown. (C) Membrane-permeable, thiol-binding tracer uptake (red dots) into the column (white arrows) via vessels (white arrowheads). (D) High-magnification view of capillary (white arrowheads) and astrocytes on and adjacent to nerve bundles with tracer uptake (red spots, white arrows.) The phase-differential configuration (b) shows the orientation of capillary and nerve bundles.