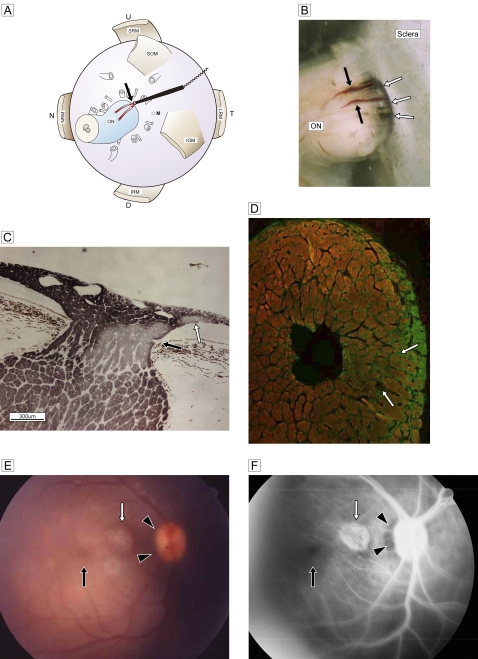
Figure 3.
(A) Schematic view of retrobulbar structure and the vessel targeted for cauterisation (red; two branches are drawn) with a bipolar disc electrode (black stick with cord) and cautery point (black arrow). (B) Stereoscopic view of the junction between the optic nerve and sclera shows the two branches of the paraoptic lateral short posterior ciliary artery (black arrows) and the cave of the site of scleral penetration (white arrows). (C) Deterioration of temporal segmental phosphorylated axons (immunostained by SMI-31; DABni) in a sagittal section at three postoperative weeks. An artery penetrates the optic nerve from the border tissue of Elschnig at the level of the pre-lamina cribrosa (black arrow). Focal retinal discolouration (white arrows in E and F) indicates a lesion caused by subretinal scarring of the recurrent artery (white arrow). (D) Double staining of glial fibrillary acidic protein (Alexa 488) with SMI-31 (Rhodamine 555) in the frontal section. Marked glial proliferation from the circumferential row is present in the temporal quadrant. (E) A fundus photograph shows the dark halo of a temporal disc margin (black arrowheads) with focal subretinal atrophy (white arrow). (F) Fluorescein angiography shows a filling defect in the temporal disc margin (black arrowheads) and a focal scar (white arrow) corresponding to the focal retinal lesion in C. The macula is normal (black arrows). D, down; IOM, inferior oblique muscle; IRM, inferior rectus muscle; LRM, lateral rectus muscle; MRM, medial rectus muscle; N, nasal; NRM, nucleus raphe magnus; M, the region of macula; ON, optic nerve; SOM, superior oblique muscle; SRM, superior rectus muscle, T, temporal; U, up.