Figure 8.
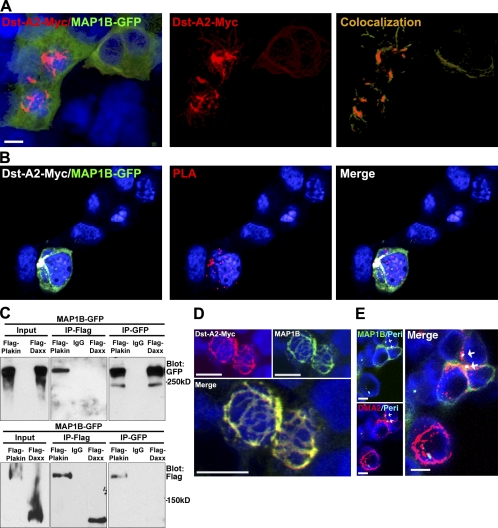
Dystonin-a2 interacts with MT-stabilizing protein MAP1B. (A) Colocalization of recombinant dystonin-a2–myc and MAP1B-GFP in 293T cells as assessed by confocal microscopy. Vector mask of colocalization shows the region of colocalization is at the perinuclear (Peri) cytoskeleton. (B) Proximity ligation assay (PLA) of recombinant dystonin-a2 and MAP1B-GFP shows that the two proteins are within 3 Å of each other. (C) Reciprocal GFP/FLAG pull-down of MAP1B and the plakin domain of dystonin shows that MAP1B and dystonin interact via the plakin domain. (D) Confocal microscopy of dystonin (Dst)-a2–myc and endogenous MAP1B shows colocalization in perinuclear regions of the cell. (E) Colocalization analysis of recombinant dystonin-a2–myc and MAP1B-GFP combined with antigenic labeling of pericentrin by confocal microscopy shows that the interaction occurs in a subcellular region surrounding the centrosome (arrows). IP, immunoprecipitation. Bars, 10 µm.