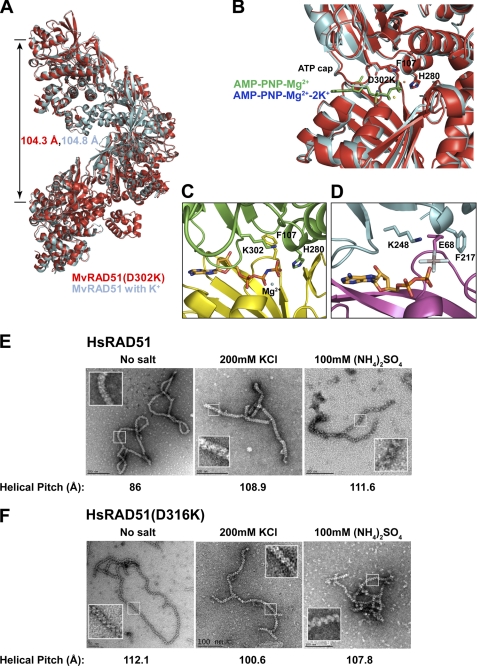
FIGURE 6.
Structural comparison of MvRAD51 and RAD51 ATP cap Asp → Lys substitution mutation. A, superimposed filament assembly of active wild type MvRAD51 structure in the presence of K+ cations (cyan) (PDB code 1XU4) and MvRAD51(D302K) (red) (PDB code 3NTU). Helical pitch is indicated with the respective color. B, enlarged view of the intersubunit ATP binding region of active wild type MvRAD51 and MvRAD51(D302K). Relative location of AMP-PNP-Mg2+-2K+ of the wild type MvRAD51 (blue) and the AMP-PNP-Mg2+ of the MvRAD51(D302K) (green) are shown. C, ATP cap region of MvRadA(D302K). Phe-129 and His-280 are in active form conformation. γ-phosphate group of ATP analog forms a direct interaction with ϵ-amino group of Lys-302. D, active filament form of E. coli RecA. Lys-248 of the ATP cap forms a direct contact with the ALF4− group of the ATP analog (PDB code 3CMU). Electron microscopy analysis of nucleoproteins filaments of wild type HsRAD51 (E) and HsRAD51(D316K) (F) with ssDNA. Reaction conditions and product visualization are described under “Experimental Procedures.” Reaction conditions are indicated above each EM image, and the corresponding helical pitch is indicated below. Insets indicate enlarged images of the helical configuration.