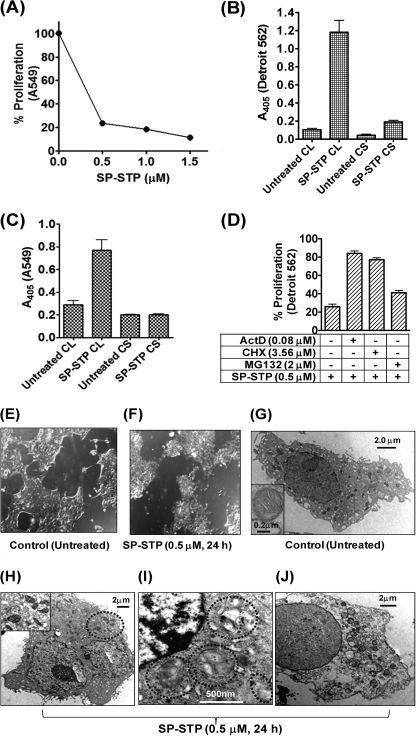
FIGURE 3.
SP-STP-mediates apoptosis and not necrosis of human respiratory cells. A, MTT assay demonstrating the dose-dependent effect of the purified recombinant SP-STP on the proliferation of A549. B and C, absorbance (405 nm)-based cell-death detection assay depicting the presence or absence of nucleosomal fragments in the culture supernatant (CS) and corresponding cell lysates (CL) of Detroit 562 (B) and A549 cells (C) to monitor the extent of necrosis and apoptosis in SP-STP-treated cells. D, MTT assay demonstrating the effect of transcription inhibitor actinomycin D (ActD), protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX), and proteasome inhibitor (MG132) on SP-STP-mediated proliferation inhibition of Detroit 562 cells. The proliferation of cells treated with the inhibitors alone in each case was taken as control. E and F, differential interference contrast images obtained by light microscopic analysis of pharyngeal cells upon SP-STP (0.5 μm, 24 h) treatment. Ultrastructural analysis of untreated (G) and SP-STP-treated (H–J) Detroit 562 cells. Apoptotic Detroit 562 cells showing: H, severely damaged mitochondria; I, nuclear indentations, prominent autophagic membranes/vacuoles (dotted circles), and incipient chromatin condensation. J, late-stage apoptotic cell with loss of cellular organelles. Scale bars show indicated measurement.