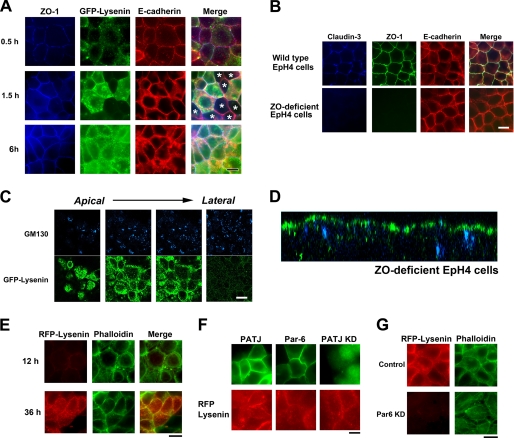
FIGURE 4.
Asymmetric sphingomyelin clusters are retained in the absence of TJs. A, EpH4 cells were cultured overnight in low Ca2+ medium, and their polarization was initiated by transferring to normal Ca2+ medium. After a 0.5-, 1.5-, or 6-h incubation, cells were fixed and stained with anti-ZO-1 mAb (blue), GFP-lysenin (green), and anti-E-cadherin mAb (red). In some cells TJs were formed based on the staining of ZO-1 before apical sphingomyelin cluster formation (asterisks, middle panel) (scale bar, 10 μm). B, EpH4 cells and ZO-deficient EpH4 cells were fixed and stained with anti-claudin-3 polyclonal antibody (blue), anti-ZO-1 mAb (green), and anti-E-cadherin mAb (red) (scale bar, 10 μm). C, ZO-deficient EpH4 cells were fixed and stained with GFP-lysenin (green) and anti-GM130 mAb (blue). The asymmetric lysenin staining was maintained in ZO-deficient EpH4 cells (scale bar, 10 μm). D, xz section of a confocal image of B is shown. E, ZO-deficient cells were cultured in low Ca2+ medium overnight, and their polarization was initiated by transferring to normal Ca2+ medium. After a 12- or 36-h incubation, cells were fixed and stained with RFP-lysenin (red) and phalloidin (green) (scale bar, 20 μm). F, EpH4 cells were transfected with a Myc-tagged PATJ expression vector (top), a Myc-tagged Par-6A expression vector (middle), or a vector that simultaneously produces shRNA against PATJ and expresses GFP (bottom). Cells were stained with anti-Myc mAb (green) (top, middle) and RFP-lysenin (red) (scale bar, 10 μm). G, EpH4 cells were transfected with a control H1 promoter vector (top) or a vector that produces shRNA against Par-6 (bottom). KD, knock down. Cells were fixed and stained with RFP-lysenin (red) and phalloidin (green) (scale bar, 10 μm).