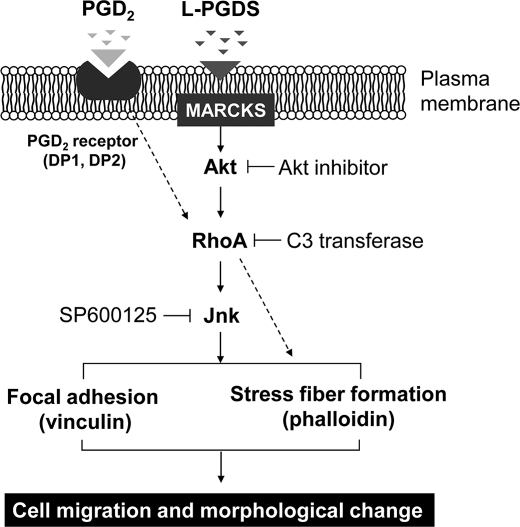
FIGURE 14.
Possible mechanisms underlying L-PGDS-induced cell migration and morphological changes. L-PGDS promotes glial cell migration and morphological change via MARCKS in plasma membrane. L-PGDS·MARCKS complex may activate AKT, which in turn activates the RhoA. Activated RhoA may induce JNK activation and actin polymerization. Subsequently, JNK may induce focal adhesion formation through phosphorylation of focal adhesion molecules such as vinculin. In the mean time, PGD2 may exert similar effects through DP1 or DP2 and Rho pathways. L-PGDS, however, acts independently of PGD2 or PGD2 receptors.