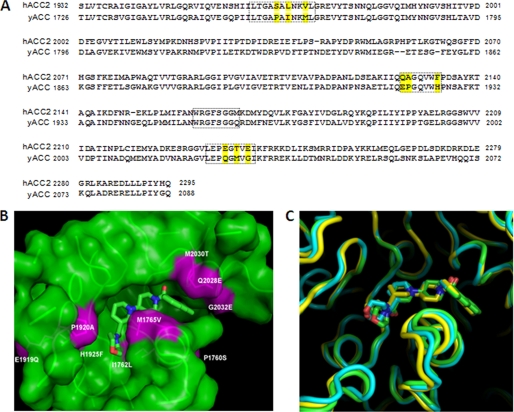
FIGURE 2.
Comparison of yeast (yCT), human (hCT), and humanized (yCT-H9) CT domain active site residues. A, sequence alignment of human ACC2 and yeast ACC-CT domain residues was performed using ClustalW (30). Residues in the boxed area are those within 6 Å of the inhibitor (Compound 1) (17). The yellow-highlighted residues are the ones that differ between human and yeast at the ligand binding interface. B, shown is molecular surface of the binding site for compound 1 in the yeast CT domain. The yeast active site residues that were mutated to mimic the human ACC-CT domain (nine point mutants as reported in “Experimental Procedures”) are colored in magenta. The structure of Compound 1 (PDB code 1W2X) is depicted as green sticks. C, the active site region of yCT structure (green ribbon) was superimposed on the corresponding structures of hCT (yellow ribbon) and yCT-H9 (cyan ribbon). The binding mode of Compound 1 to yCT (green stick), yCT-H9 (cyan stick), and hCT (yellow stick) was superimposed to show the relative positions.