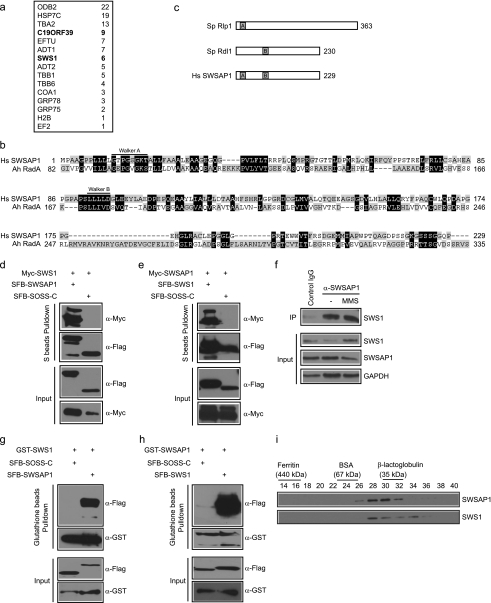
FIGURE 1.
Identification of SWSAP1 as hSWS1-binding protein. a, 293T cells stably expressing SFB-tagged (S-tag, FLAG epitope tag, and streptavidin-binding peptide tag) hSWS1 was used for tandem affinity purification of protein complexes isolated from chromatin fractions. Tables are summaries of proteins identified by mass spectrometry analysis. Letters in bold indicate the bait proteins. b, alignment of human SWSAP1 with Arcanobacterium hemolyticum RadA. The conserved Walker A and Walker B motifs are indicated. c, schematic representation of fission yeast Rlp1, Rdl1, and human SWSAP1. d and e, the interaction between hSWS1 and SWSAP1 was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments. 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-tagged hSWS1 or SWSAP1 together with plasmids encoding SFB-tagged SWSAP1 or hSWS1 as indicated. Cells were collected 24 h after transfection. Precipitation reactions were performed using S beads, and immunoblotting was carried out using antibodies as indicated. f, endogenous hSWS1 and SWSAP1 form a complex in vivo. HeLa cells were mock treated or treated with MMS. Control or anti-SWSAP1 immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-hSWS1 antibody (top). The expression levels of endogenous proteins were revealed by immunoblotting using anti-hSWS1 and anti-SWSAP1 antibodies (bottom). g and h, hSWS1 and SWSAP1 directly bind to each other. SF9 cells were co-infected with baculoviruses expressing GST-tagged hSWS1 or SWSAP1 together with those expressing SFB-tagged SWSAP1 or hSWS1. Pulldown experiments and immunoblotting were carried out as indicated. i, heterodimeric complex formation was studied by gel filtration chromatography as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Aliquots from peak fractions were analyzed on 12.5% SDS-PAGE and confirmed by Western blot analysis.