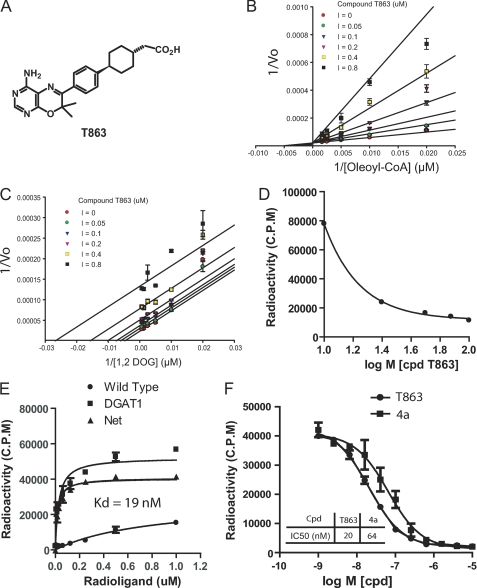
FIGURE 2.
, Biophysical characterization of DGAT1 inhibitors. A, structure of T863. B and C, Lineweaver-Burk plots for oleoyl-CoA or 1,2-DOG in the presence of T863 at various concentrations. The data were obtained from the CPM fluorescent assay performed in the 384-well format as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The pattern of fitting curves suggests that T863 is competitive against oleoyl-CoA (B) and uncompetitive against 1,2-DOG (C). D, T863 competes with the binding of acyl-CoA to hDGAT1 microsomes in a dose-dependent manner. Increasing concentrations of T863 were incubated with 50 μm [14C]oleoyl-CoA and DGAT1 microsomes containing 0.5 μg of total protein in 100 μl of reaction mixture. Filtration was performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” E, the radiolabeled DGAT1 inhibitor T863 shows specific binding to hDGAT1 microsomes. 3H-Labeled T863 at various concentrations was incubated with wild-type or DGAT1-overexpressing Sf-9 cell microsomes for 90 min, followed by filtration to remove unbound radioligand. Retained radioligand was detected with a liquid scintillation counter. F, DGAT1 inhibitors T863 and compound 4a compete with the radiolabeled [3H]T863 for binding to hDGAT1. Increasing concentrations of compound T863 or 4a were incubated with DGAT1-microsomes and [3H]T863 for 90 min before filtration. See “Experimental Procedures” for a detailed description of the radioligand filtration assay. Data represent mean ± S.E. (error bars) obtained from three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.