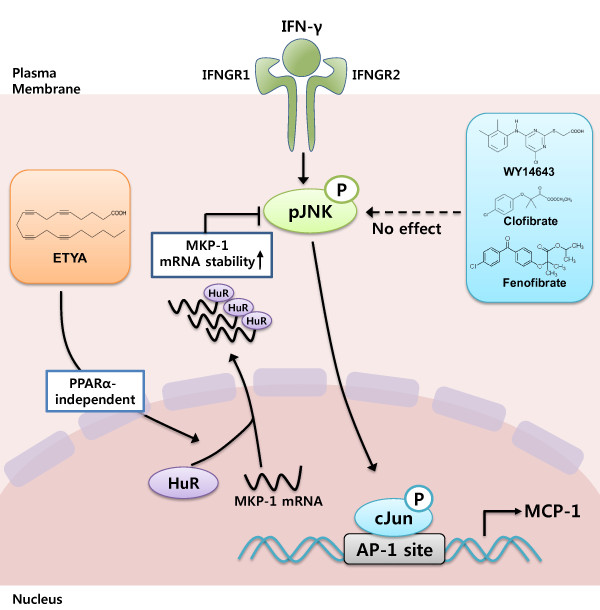
Figure 6.
A model showing the anti-inflammatory mechanism of ETYA in IFN-γ-stimulated glial cell. IFN-γ induces JNK/Jun phosphorylation and increases CCL2/MCP-1 gene expression. ETYA, but not fibrates, increases MKP-1 mRNA stability by inducing HuR cytoplasmic shuttling, and thereby suppresses IFN-γ-induced JNK signaling and CCL2/MCP-1 expression.