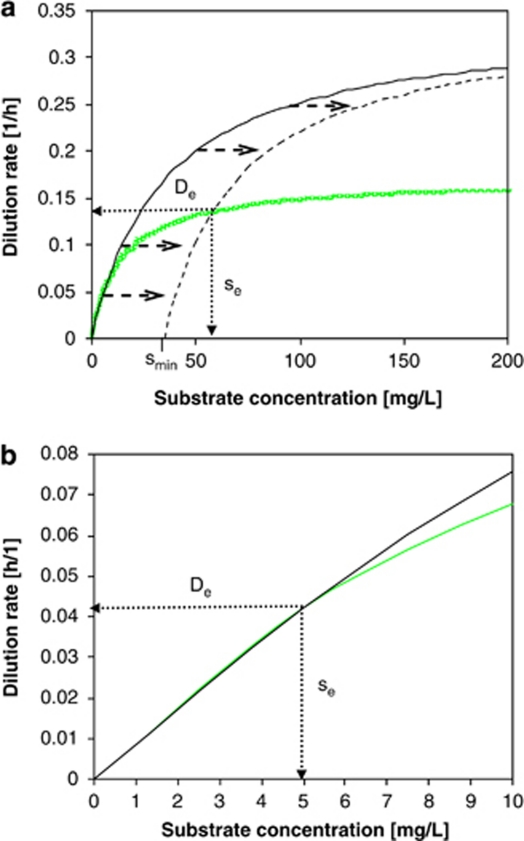
Figure 5.
(a) μ–s relationship of E. coli (using original Monod model (—) and Monod model extended with smin (- - -)) and C. heintzii (Monod model ( )). All parameters were determined at D=0.075 h−1. C. heintzii will outcompete E. coli at s<se, whereas E. coli will outcompete C. heintzii at s>se. Coexistence is theoretically possible at De with a steady-state substrate concentration se. Kinetic parameters of the two competitors are listed in Table 2. (b) Zoom into the 0–10 μg l−1 concentration range of Figure 5a. At very low substrate concentration (0–5 μg l−1), the classical Monod kinetics predicts for both strains virtually the same specific growth rates and se is 5.0 μg l−1 suggesting coexistence, which is in contradiction to the competition experiments shown in Figure 2a.
)). All parameters were determined at D=0.075 h−1. C. heintzii will outcompete E. coli at s<se, whereas E. coli will outcompete C. heintzii at s>se. Coexistence is theoretically possible at De with a steady-state substrate concentration se. Kinetic parameters of the two competitors are listed in Table 2. (b) Zoom into the 0–10 μg l−1 concentration range of Figure 5a. At very low substrate concentration (0–5 μg l−1), the classical Monod kinetics predicts for both strains virtually the same specific growth rates and se is 5.0 μg l−1 suggesting coexistence, which is in contradiction to the competition experiments shown in Figure 2a.