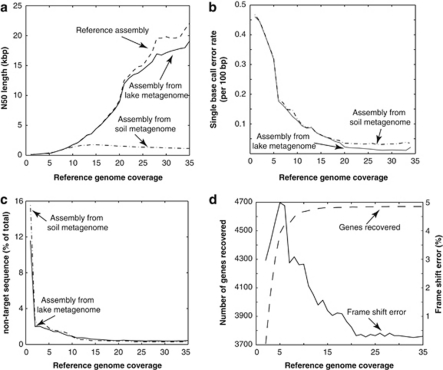
Figure 1.
Sequence errors and artifacts in assembled contigs of a target genotype from a complex metagenome. The assembly of a reference genome (Escherichia sp. TW10509) based solely on its own reads (reference assembly) was compared with the assembly of the genome from the in silico metagenome, which was composed of Lanier.Illumina spiked in with reads of the reference genome. (a) Comparison of N50, that is, the contig length that 50% of the entire assembly is contained in contigs no shorter than this length, between the latter and the reference assemblies over different reference genome coverage (abundance). (b) Single base call error rate decreased dramatically as reference genome abundance in the metagenome increased and reached a plateau at about 20 × coverage. (c) At low coverage, contigs from the metagenome assembly had a substantial portion of non-targeted (chimeric) sequences. (d) Frequency of frameshift errors as a function of the reference genome abundance. Results from similar analyses using a higher-complexity (Supplementary Figure S9) soil metagenome of similar size to the Lanier.Illumina metagenome are also shown for comparison.