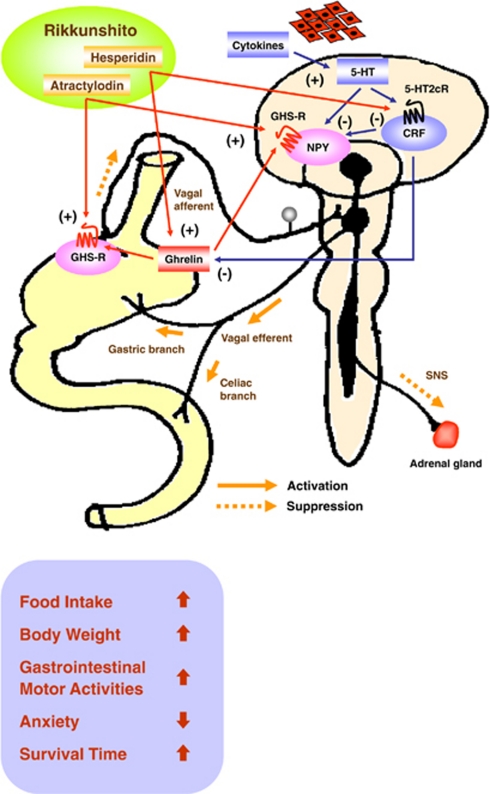
Figure 5.
Ghrelin signaling and cancer anorexia–cachexia. Hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) neurons are activated by cytokines through serotonin (5-HT) and the 5-HT 2c receptor (5-HT2cR), which shows functional divergence.15 Our data demonstrate the existence of a novel 5-HT-CRF neuronal pathway that inhibits ghrelin secretion and has a pathogenetic role in cancer anorexia–cachexia syndrome. The traditional herbal medicine rikkunshito improves anorexia, weight loss, gastrointestinal (GI) dysmotility, anxiety-related behavior and survival. Rikkunshito and its active component hesperidin stimulate ghrelin secretion from stomach by interrupting this 5-HT-CRF pathway via 5-HT2cR antagonism. Another active component atractylodin potentiates the action of ghrelin by presumably allosterically sensitizing the GHS-R on the vagal afferent terminals of stomach or neuropeptide Y (NPY) neurons of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC). The 5-HT2cR antagonist improved anorexia–cachexia in the short term, but failed to improve survival. Thus, both the release of ghrelin and the potentiation of ghrelin/GHS-R signaling are important for mitigating ghrelin insufficiency and resistance, which are characteristics of cancer anorexia–cachexia syndrome.