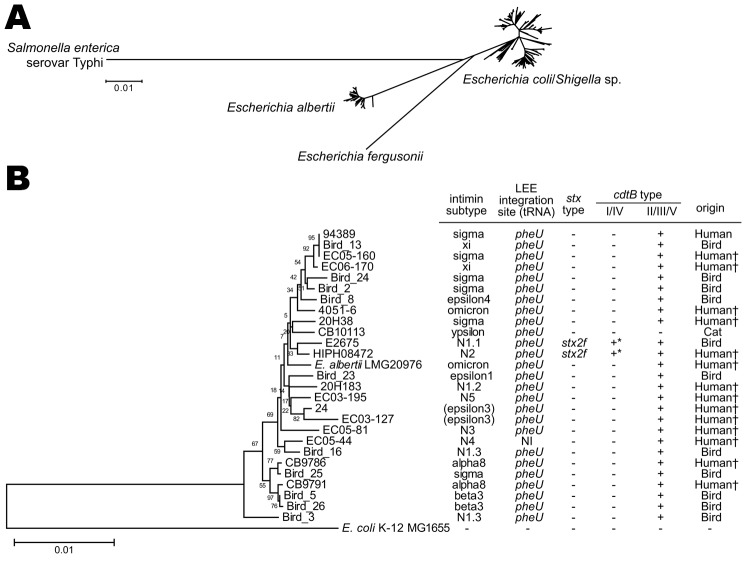
Figure 2.
Neighbor-joining tree of 179 eae-positive Escherichia coli and Escherichia albertii strains analyzed by multilocus sequence analysis. The tree was constructed with the concatenated partial nucleotide sequences of 7 housekeeping genes (see Technical Appendix for protocol details). A) The whole image of the 179 strains examined and 10 reference strains (E. coli/Shigella sp., E. fergusonii, and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi) is shown. B) Enlarged view of the E. albertii lineage and the genetic information of the identified E. albertii strains. E. coli strain MG1655 and E. albertii type strain LMG20976 are included as references. There was no phylogenetic correlation between human and animal isolates. The cdtB genes indicated by * are classified as subtype I. The strains indicated by † were isolated from patients with signs and symptoms of gastrointestinal infection. LEE, locus of enterocyte effacement; NI, not identified; NA, not applicable Scale bars indicate amino acid substitutions (%) per site.