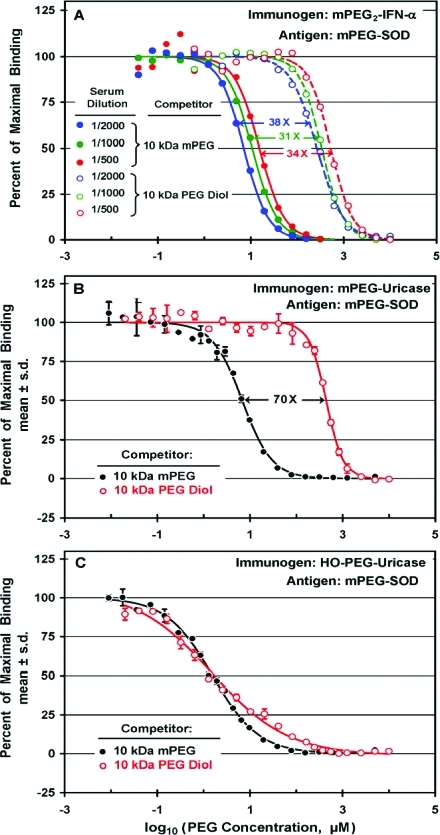
Figure 6.
Competitive ELISAs were used to compare the inhibition by mPEG and by PEG diol (HO-PEG-OH) of the binding to mPEG-SOD of antibodies raised against mPEG2-IFN-α (A), against mPEG-uricase (B), and against HO-PEG-uricase (C). Concentrations of competitors are expressed as micromolar PEG in the serum-containing assay mixtures. (A) Anti-PEG antibodies in serum from a rabbit immunized with mPEG2-IFN-α bound 10 kDa mPEG (filled circles) 30-fold to 40-fold more tightly than 10 kDa PEG diol (open circles), regardless of the serum dilution in the range of 1/500 to 1/2000. (B) Anti-PEG antibodies in serum from a rabbit immunizedwith mPEG-uricase bound 10 kDa mPEG (●) c. 70 times more tightly than 10 kDa PEG diol (○). The serum was diluted 1/1000. (C) Competitive ELISAs of anti-PEG antibodies in serum from a rabbit immunized with HO-PEG-uricase revealed no preferential binding of 10 kDa mPEG (●) compared to 10 kDa PEG diol (○), although the slopes of the competition curves differed. The serum was diluted 1/500.