Figure 2.
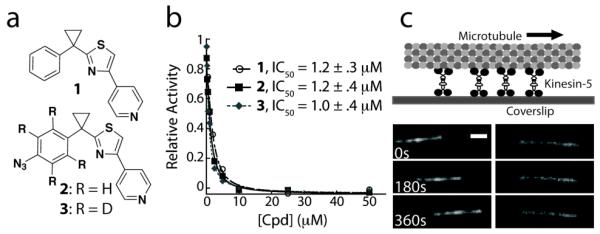
(a) Chemical structure of an ATP-competitive kinesin-5 inhibitor and analogs generated for SILIC. (b) Potency of compounds 1, 2 and 3 in inhibiting kinesin-5 activity, as examined using a steady-state microtubule-stimulated ATP hydrolysis assay. (c) In the presence of MgATP (1 mM) and DMSO, homotetrameric kinesin-5 drives microtubule gliding at an average rate of 19.6 ± 4.5 nm/s (left panel, n > 25). 1 (50nM) inhibits this activity (right panel, n > 30). Scale bar is 2μm.
