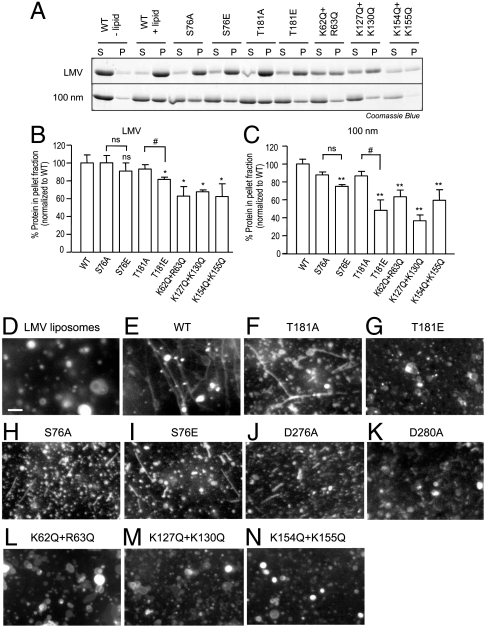
Fig. 3.
Syndapin I phosphosites affect lipid binding and tubulation. (A) Protein–lipid binding of syndapin I F-BAR mutants were examined. Purified syndapin I F-BAR wild-type (WT) and point mutant proteins (5 μg) were incubated with synthetic large multilamellar vesicles (LMV) or uniform 100-nm liposomes (50 μg) made of 60% L-α-phosphatidyl-L-serine (PS), 20% L-α-phosphatidyl-L-choline (PC), and 20% L-α-phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). Samples were centrifuged and the supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions were analyzed using SDS/PAGE followed by Coomassie Blue staining. (B and C) Quantitative representation of A. Three independent experiments were performed and the protein band intensity was measured. The error bars indicate standard error of the mean (± SEM, n = 3). A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied: ∗ P < 0.05 against WT, #P < 0.05 against A mutants, ns = non-significant. (D–N) In vitro protein–lipid tubulation of syndapin I F-BAR mutants. LMV (50 μg) containing 60% PS, 20% PC, 10% PE, and 10% fluorescein-conjugated PE were incubated with purified syndapin I F-BAR-WT, and point mutant proteins. Lipid tubulation was analyzed via fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. Images are representative of at least two independent experiments.