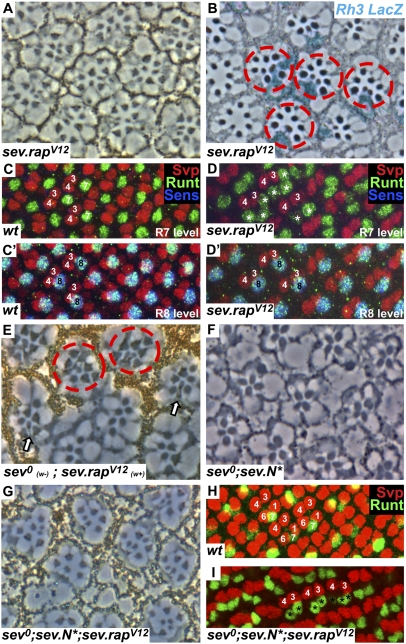
Fig. 3.
Activated Rap specifies R7 photoreceptors. (A) A section through a sev.rapV12 homozygous eye shows multiple small rhabdomeres. (B) A tangential section through an X-Gal–stained sev.rapV12 eye in an Rh3–lacZ reporter background. Subsets of R7 cells and supernumerary R7 cells are stained in blue (red circles). (C and C′) Posterior region of a wild-type eye disk stained with Svp (red), Runt (green), and Sens (blue). Each ommatidium has a single apical Runt-labeled R7 (C) and a single basal Runt- and Sens-stained R8 (C′). (D and D′) A sev.rapV12 eye disk stained as in C showing multiple R7 cells (asterisks) in the apical level and a single R8 basally. (E) A tangential section through a sev0 mutant eye in which a clone of sev.rapV12 has been induced marked by pigment. In the pigmented region, ommatidia containing multiple R7 cells are evident (red circles), and at the mosaic interface normally constructed ommatidia form carrying pigmented (sev.rapV12) R7 cells (arrows). (F) A tangential section through a sev0;sev.N* eye (reproduced from ref. 13) showing the absence of R7 cells. (G) When RapV12 is added to this background (sev0;sev.N*;sev.rapV12) R7 cells are restored. (H) Image of a wild-type eye disk at the region where R1/6 precursors label with Svp (red). (I) In the sev0;sev.N*;sev.rapV12 background, R1/6 precursors no longer express Svp but now express Runt (green), indicating their differentiation into R7 photoreceptors (marked by asterisks).