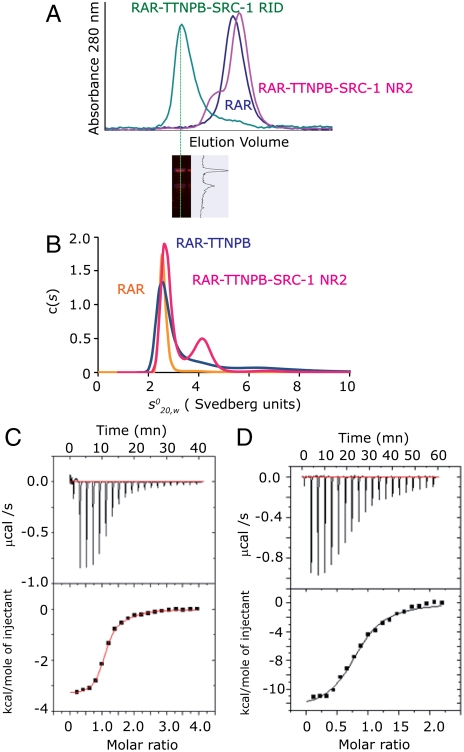
Fig. 3.
Coactivator bound-RARβ LBD forms homodimers in solution. (A) Gel filtration profile of apo RARβ LBD and the TTNPB complexes with SRC-1 NR2 or SRC-1 RID showing that two oligomeric species are observed in presence of the peptide and only one species in presence of the RID. (Bottom) SDS gel stained by quantitative Sypro-Ruby of the RARβ-SRC-1 RID fraction that indicates a stoichiometry of 1 RID for 2 RARβ. (B) Sedimentation velocity analysis for RARβ LBD apo and its complexes with TTNPB and SRC-1 NR2 peptide by Lamm equation fits using the Sedfit program. The sedimentation distribution plots show one sedimentation species for the apo RARβ LBD and the TTNPB complex with a sedimentation coefficient 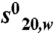 of 2.6 ± 0.1 Svedberg units. The calculated molecular mass value is 29 kDa and corresponds to the monomer. In presence of ligand (TTNPB or 9-cis RA) and SRC-1 NR2 peptide, two peaks are observed, one corresponding to the monomer (
of 2.6 ± 0.1 Svedberg units. The calculated molecular mass value is 29 kDa and corresponds to the monomer. In presence of ligand (TTNPB or 9-cis RA) and SRC-1 NR2 peptide, two peaks are observed, one corresponding to the monomer (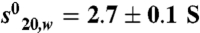 ; Mw = 31 kDa) and the second to the dimer (
; Mw = 31 kDa) and the second to the dimer (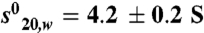 (Mw = 58 kDa). (C–D) Representative ITC titrations of SRC-1 NR2 peptide (C) and SRC-2 RID (D) into RARα LBD. RARα LBD binds SRC-1 NR2 with a stoichiometry of two peptides per homodimer and a dissociation constant Kd of 1.5 μM, whereas in the case of SRC-1 RID, RARα binds with a stoichiometry of 1 RID per homodimer and a Kd of 2.5 μM.
(Mw = 58 kDa). (C–D) Representative ITC titrations of SRC-1 NR2 peptide (C) and SRC-2 RID (D) into RARα LBD. RARα LBD binds SRC-1 NR2 with a stoichiometry of two peptides per homodimer and a dissociation constant Kd of 1.5 μM, whereas in the case of SRC-1 RID, RARα binds with a stoichiometry of 1 RID per homodimer and a Kd of 2.5 μM.