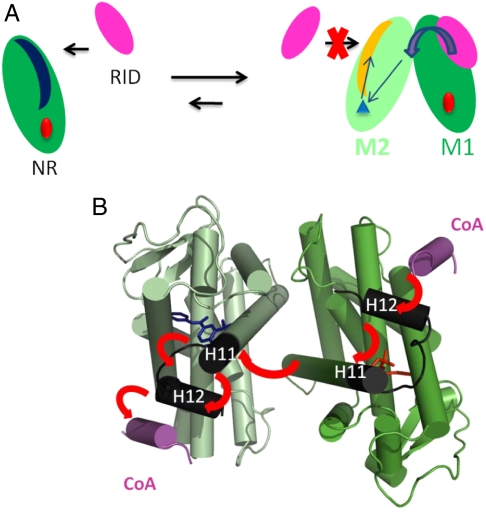
Fig. 6.
Proposed mechanism for the allosteric control by coactivator binding to nuclear hormone receptors. (A) Binding of the NR interacting domain RID to NR monomer M1 triggers the formation of dimers with an induced conformational change of the C-terminal end of monomer M2 and its ligand. Consequently, the binding of the CoA on M2 is affected. (B) Molecular level representation of our proposed mechanism of allosteric regulation.