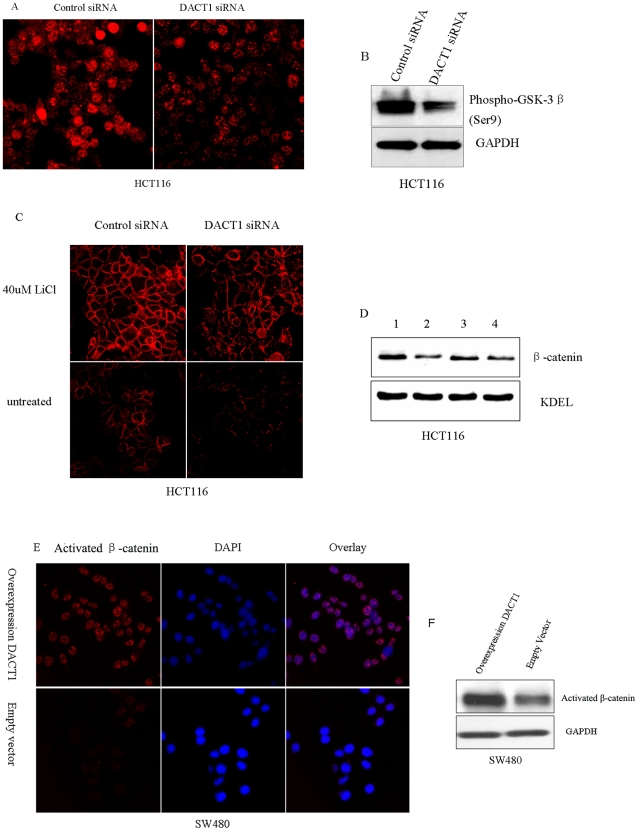
Figure 9. DACT1 affects the subcellular localization of β-catenin through interacting with GSK-3β.
(A) Photomicrographs of control siRNA and DACT1 siRNA expressing HCT116 cells immunostained with an anti-phospho-GSK-3β(Ser9) antibody (red). Silencing of DACT1 in HCT116 cells decreases levels of phospho-GSK-3β(Ser9). (B) Representative Western blots of HCT116 cells expressing control siRNA and DACT1 siRNA. Silencing of DACT1 in HCT116 cells decreases levels of phospho-GSK-3β(Ser9). GAPDH was used as the loading control. (C) HCT116 cells expressing control siRNA and DACT1 siRNA were treated for 1 h with GSK-3β inhibitory drugs (40 mM LiCl). Cells were stained and analyzed by microscopy to detect the expression of β-catenin. LiCl treatment of HCT116 cells increases the levels of β-catenin at the plasma membrane. (D) Representative Western blots of LiCl-treated HCT116 cells, which express either control siRNA or DACT1 siRNA. LiCl treatment of HCT116 cells increases levels of β-catenin at the plasma membrane. KDEL was used as a loading control. 1: HCT116 cells expressing control siRNA that had been treated with 40 mM LiCl for 1 h. 2: HCT116 cells expressing control siRNA that had not been treated with LiCl. 3: HCT116 cells expressing DACT1 siRNA that were treated by 40 mM LiCl for 1 h; 4: HCT116 cells expressing DACT1 siRNA that had not been treated with LiCl. (E) Photomicrographs of control siRNA and DACT1 siRNA expressing HCT116 cells immunostained with an anti-phospho-GSK-3β(Ser9) antibody (red). Silencing of DACT1 in HCT116 cells decreases levels of phospho-GSK-3β(Ser9). (F) Representative Western blots of HCT116 cells expressing control siRNA and DACT1 siRNA. Silencing of DACT1 in HCT116 cells decreases levels of phospho-GSK-3β(Ser9). GAPDH was used as a loading control.