Figure 8.
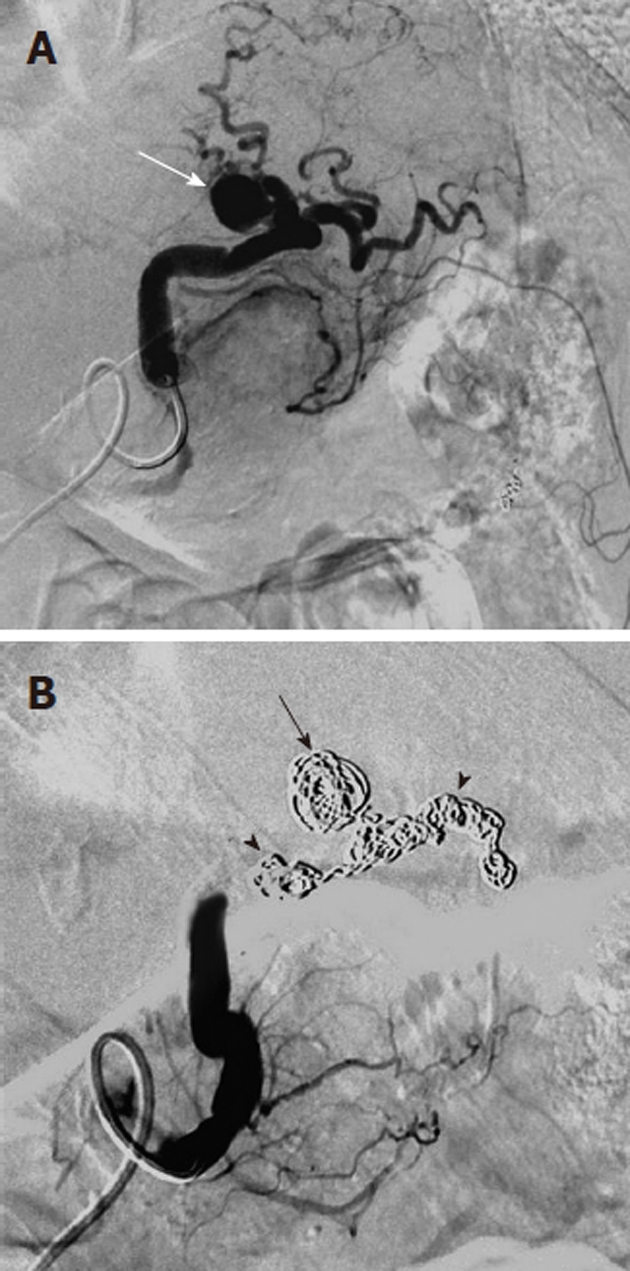
Transcatheter treatment of a pancreatitis related pseudoaneurysm. A: Selective splenic artery digital subtraction angiography arteriogram shows that the pseudoaneurysm (white arrow) arises directly from the splenic artery; B: Coil embolization of the pseudoaneurysm (black arrow) and of the splenic artery (black arrowheads) both proximal and distal to the pseudoaneurysm was successful in controlling the hemorrhage. Arterial pseudoaneurysms associated with pancreatitis have a significant risk of rupture; if this occurs there is an extremely high mortality rate.
