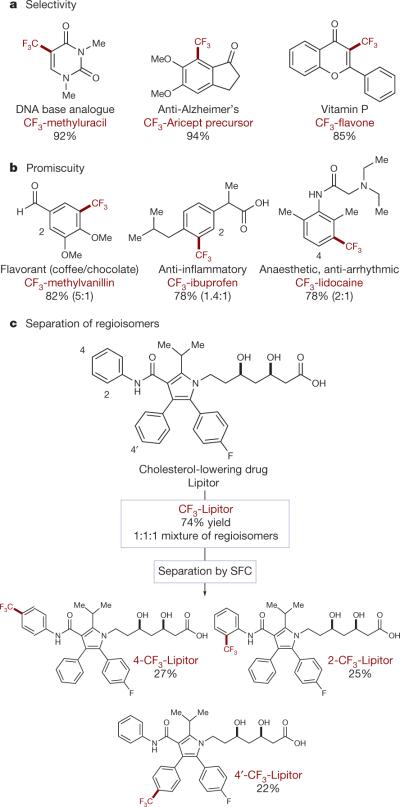
Figure 4. Direct trifluoromethylation of biologically active molecules.
Subjecting common medicinal agents and other biologically active molecules to our standard photoredox protocol enables direct CF3 installation selectively at metabolically susceptible positions of some molecules (a). Alternatively, C–H functionalization of more metabolically stable medicines occurs non-selectively, allowing for rapid access to drug analogues (b). The promiscuous modification of equally reactive π-systems, such as the arenes in Lipitor, may be followed by separation of isomers (for example, via supercritical fluid chromatography, SFC) for rapid screening of biological activity (c).