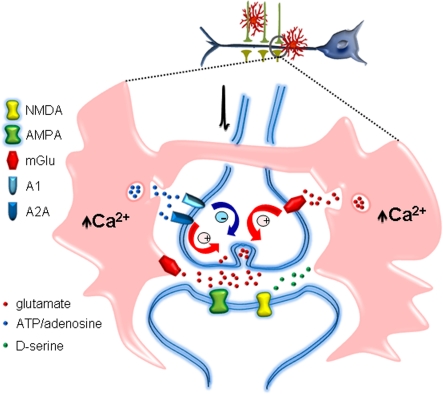
Figure 4. Astrocytes modulate synaptic transmission.
Astrocyte calcium signal triggered by synaptic activity stimulates the release of different gliotransmitters, such as glutamate, ATP/adenosine or d-serine. These gliotransmitters act on specific glutamate α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA), NMDAR and mGluR and adenosine (A1 and A2A) receptor types localized at the pre- or post-synaptic neurons. The consequently activated intracellular signalling pathways lead to depression or potentiation of synaptic transmission.