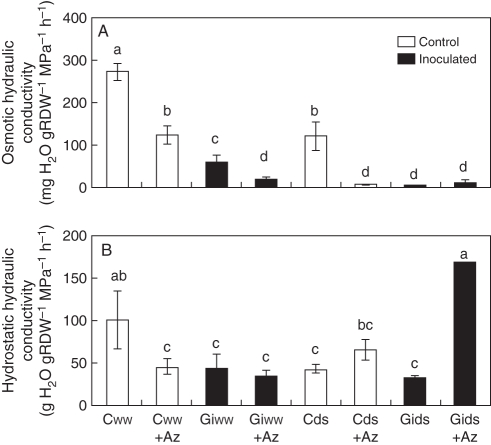
Fig. 3.
Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbiosis, drought stress and sodium azide treatment on (A) osmotic root hydraulic conductivity and (B) hydrostatic root hydraulic conductivity, in maize plants grown under conditions of experiment 2 (RDW = root dry weight). Treatments are designed as uninoculated controls (C, open bars) or G. intrarradices-inoculated plants (Gi, black bars). Plants were cultivated under well-watered conditions (ww) or subjected to drought stress (ds). A group of plants within each treatment was treated with 7 mm sodium azide (+Az) before measurement of hydraulic conductivity. Bars represent means plus standard error (n = 6). Means followed by different letters are significantly different (P < 0·05) as determined by Duncan's multiple range and LSD tests.