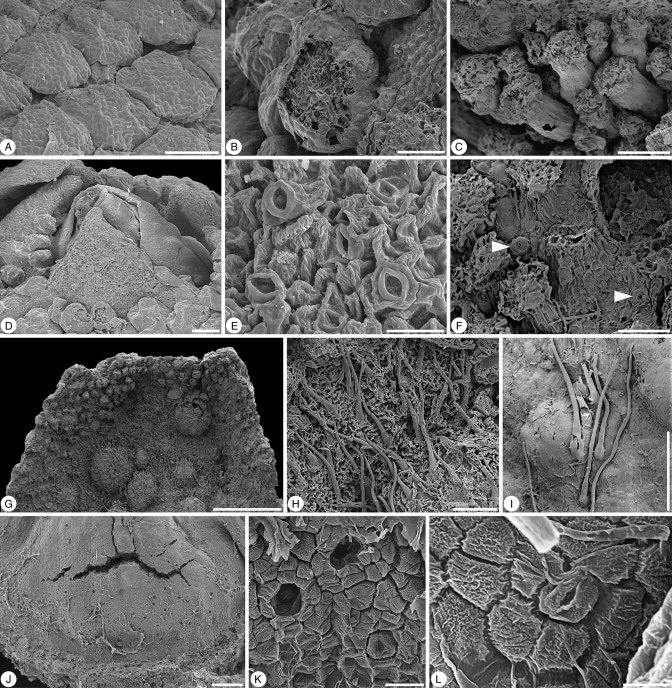
Fig. 2.
Glandulocalyx upatoiensis. Surface details of sepals, petals and gynoecium. (A) Well-developed, densely spaced multicellular trichomes on the abaxial surface of the sepals; PP55153 (holotype). (B) Abraded trichome from abaxial surface of sepal showing multicellular internal structure; PP55155. (C) Stalked multicellular trichomes at the base of a sepal; PP55158. (D) Close-up of apex of a floral bud showing sepal tips that are free of multicellular trichomes surrounding the tip of the corolla with its smooth petals; PP55153 (holotype). (E) Detail of stomata from the tip of a sepal; PP55153 (holotype). (F) Stomata (arrows) scattered among multicellular trichomes on abaxial surface of sepals; PP55158. (G) Adaxial surface in the distal half of a sepal showing multicellular trichomes at the periphery and simple, unicellular trichomes in the centre; note blisters formed during charcoalification; PP55155. (H) Detail of simple, unicellular trichomes on adaxial surface of sepal; PP55158. (I) Simple, unicellular trichomes on abaxial surface of petal; PP55158. (J) Base of ovary with stomata (nectary?); PP55155. (K) Detail of partly collapsed stomata at base of ovary; PP55155. (L) Detail of individual stoma at base of ovary, PP55155. Scale bars (A, C, D, I, J) = 100 µm; (B, F, H) = 50 µm; (E) = 20 µm; (G) = 500 µm; (L) = 5 µm; (K) = 10 µm.