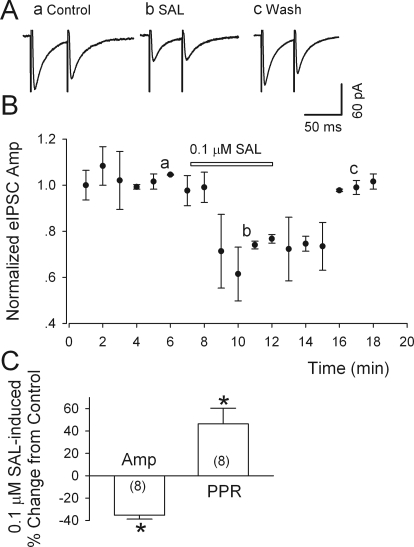
Fig. 3.
Salsolinol depresses eIPSCs in putative dopamine neurons. A, salsolinol (0.1 μM) sharply reduced the peak amplitude of both the first and second IPSC evoked by paired stimulation (at 50-ms interval) within the VTA, but the greater relative reduction of the first response increased the ratio of IPSC2/IPSC (PPR). Labels a-c refer to times in B. B, time course of salsolinol-induced changes in eIPSC amplitude (Amp). C, summary of the effects of salsolinol (0.1 μM) on the amplitude and the PPR of eIPSCs; numbers of recorded neurons are in parentheses. *, p < 0.01, paired t test for salsolinol application versus presalsolinol control. All IPSCs were recorded from putative dopamine neurons at a VH of −70 mV in the presence of APV (50 μM) and DNQX (20 μM).