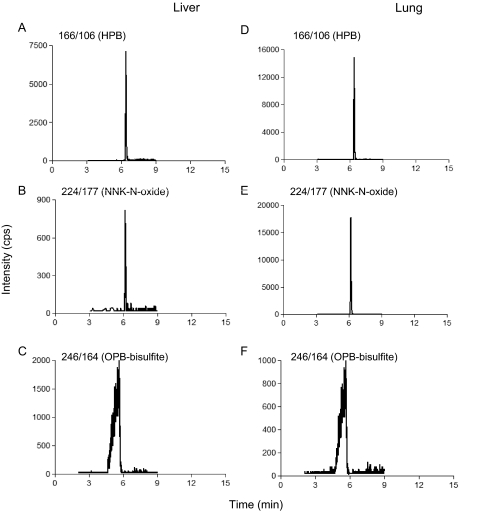
Fig. 1.
Typical LC-MS chromatograms for detection of NNK metabolites. Extracted LC-MS chromatograms for individual metabolites detected in reactions with liver (A–C) and lung (D–F) microsomes from WT mice, obtained in the MRM scan mode for quantitative analysis of metabolite levels, are shown for HPB (A and D), NNK-N-oxide (B and E), and OPB-bisulfite (C and F), with NNK substrate concentration at 2.5 μM. The chromatograms for OPB-bisulfite were obtained under acidic conditions, whereas those for HPB and NNK-N-oxide were obtained under neutral conditions. Microsomal incubations were performed without (negative controls) or with NADPH, and sodium bisulfite was added to some samples to trap OPB, as described under Materials and Methods. No signal was detected when NADPH was omitted from the incubations (data not shown). The parent/product ion pairs of m/z 166/106 (for HPB), m/z 224/177 (for NNK-N-oxide), and m/z 246/164 (for bisulfite-trapped OPB) were monitored. Metabolite identification using the MIM-EPI acquisition mode and the resultant MS/MS product-ion spectra of the detected metabolites are shown in Supplemental Figs. 1 and 2.