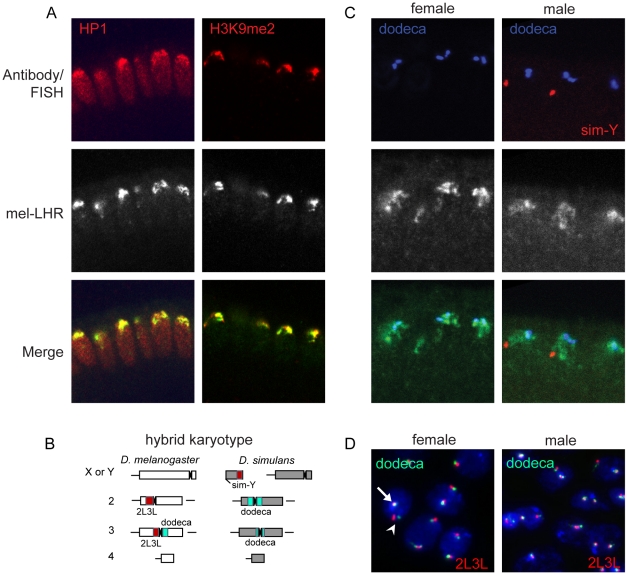
Figure 4. Normal LHR localization and organization of heterochromatin in hybrids.
(A) mel-LHR-HA (green) colocalizes with HP1 and H3K9me2 (each red), similarly to wild type (see Figure 2). (B) A schematic karyotype of a hybrid nucleus with sites of FISH probe hybridization highlighted. Red = 2L3L, blue = dodeca. (C) mel-LHR-HA (green) partially colocalizes to dodeca satellite (blue) in male and female hybrid embryos. (D) Interphase nuclei from brain cells of male and female larvae have wild type organization of the dodeca and 2L3L satellites (see Figure 3B for D. melanogaster wild type control). The orthologous second chromosomes are identifiable as a pair of adjacent red and green signals (arrowhead), while the D. melanogaster third chromosome is visible as the overlapping red and green signal (arrow). Hybrid larvae were generated from a cross between D. melanogaster yv females and D. simulans v males, and were sexed using mouth hook coloration (males are y in phenotype and females are y+).